dxiju
How Does a Wi-Fi Camera Work?
Wi-Fi cameras, also known as wireless IP cameras, are surveillance devices equipped with wireless connectivity capabilities that enable them to transmit audio and video data over a Wi-Fi network. These cameras utilize Wi-Fi technology to establish a connection with a local network, allowing users to remotely monitor and control the camera’s feed through various devices such as smartphones, tablets, or computers. Wi-Fi cameras come in various forms, including indoor, outdoor, fixed, and pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) models, catering to a wide range of surveillance needs.
Wi-Fi cameras play a crucial role in modern surveillance and monitoring systems due to their versatility, convenience, and accessibility. These cameras offer flexibility in installation, allowing users to deploy them in locations where wired connectivity is impractical or inaccessible.
Wi-Fi cameras facilitate remote monitoring, enabling users to keep an eye on their property or assets from anywhere with an internet connection. Additionally, Wi-Fi cameras often feature advanced functionalities such as motion detection, night vision, and two-way audio, enhancing their effectiveness in various surveillance applications, including home security, business monitoring, and public safety.
Understanding Wi-Fi Technology
Explanation of Wi-Fi technology and its principles
Wi-Fi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a technology standard that enables wireless communication between devices within a local area network (LAN). Wi-Fi operates based on radio frequency signals transmitted over the air, allowing devices equipped with WiFi capabilities to connect to a wireless access point (router) and communicate with each other. Wi-Fi technology utilizes the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which define specifications for wireless networking protocols and transmission methods.
Overview of Wi-Fi camera components and functionalities
Wi-Fi cameras consist of several key components, including a camera lens and image sensor for capturing video footage, a processor and memory for processing and storing data, a Wi-Fi module and antenna for wireless connectivity, and a power source for operation. These cameras are equipped with various functionalities such as motion detection, night vision, two-way audio, and remote access capabilities, which enhance their surveillance capabilities and usability.
Operating Mechanism of Wi-Fi Cameras
Transmission of data through Wi-Fi networks
Wi-Fi cameras transmit audio and video data wirelessly over a Wi-Fi network using radio frequency signals. When capturing video footage, the camera encodes the data into digital format and sends it to the wireless access point (router) via the Wi-Fi connection. The router then forwards the data to the intended recipient device, such as a smartphone or computer, allowing users to view the live feed or recorded footage remotely.
Connection establishment between the camera and a Wi-Fi router
To establish a connection with a Wi-Fi router, the Wi-Fi camera first scans for available networks and displays a list of options for the user to select from. Once the user selects the desired network and enters the appropriate credentials (e.g., network name and password), the camera initiates the connection process by sending a connection request to the router. Upon successful authentication, the camera is assigned an IP address within the local network, enabling it to communicate with other devices on the network.
Role of protocols (e.g., TCP/IP) in data transmission
Protocols such as Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) play a crucial role in facilitating data transmission between Wi-Fi cameras and other devices on the network. TCP/IP is a set of networking protocols that governs the exchange of data packets between devices connected to the internet.
When transmitting data, Wi-Fi cameras segment the video footage into packets and assign a header containing routing information, including the source and destination IP addresses. These packets are then transmitted over the network using TCP/IP, ensuring reliable and efficient delivery to the intended recipient device.
In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the components and functionalities of Wi-Fi cameras, exploring their role in modern surveillance and monitoring systems.
Camera lens and image sensor
The camera lens and image sensor are integral components of Wi-Fi cameras responsible for capturing video footage. The lens determines the field of view and focal length of the camera, while the image sensor converts light into electronic signals to generate the video image.
Wi-Fi cameras may feature various types of lenses, including fixed, varifocal, and zoom lenses, offering different levels of zoom and adjustability. The image sensor, typically a CMOS or CCD sensor, plays a crucial role in determining the camera’s resolution, low-light performance, and image quality.
Processor and memory
Wi-Fi cameras are equipped with a processor and memory to handle data processing and storage tasks. The processor processes video data, performs encoding and compression algorithms, and manages communication with other devices on the network.
The memory, consisting of RAM and flash memory, stores temporary data and firmware for the camera’s operation. The processing power and memory capacity of Wi-Fi cameras influence their performance, including the ability to stream high-definition video, support advanced features, and handle multiple simultaneous connections.
Wi-Fi module and antenna
The Wi-Fi module and antenna enable wireless connectivity between the camera and a Wi-Fi router or access point. The Wi-Fi module integrates a wireless networking chipset that supports IEEE 802.11 standards and provides the necessary hardware and firmware for wireless communication.
The antenna transmits and receives radio frequency signals, allowing the camera to establish a connection with the Wi-Fi network and communicate with other devices. Wi-Fi cameras may feature different types of antennas, including internal and external antennas, to optimize signal strength and range.
Power source and connectivity options
Wi-Fi cameras require a power source for operation, which may include wired or wireless options. Wired power sources typically involve connecting the camera to a power outlet using an AC adapter or Power over Ethernet (PoE) injector. Wireless power options, such as rechargeable batteries or solar panels, offer flexibility in installation and placement, particularly for outdoor cameras. In terms of connectivity options, Wi-Fi cameras may also feature Ethernet ports for wired network connections, allowing for additional flexibility in installation and setup.
Setup and Configuration of Wi-Fi Cameras
Installation process and hardware requirements
The installation process of Wi-Fi cameras typically involves mounting the camera in the desired location, connecting it to a power source, and configuring the camera settings. Hardware requirements may vary depending on the specific camera model and installation environment.
For indoor cameras, installation may involve mounting the camera on a wall or ceiling using screws or adhesive mounts. Outdoor cameras may require additional weatherproofing measures and mounting brackets to protect against environmental elements.
Configuration through a web interface or mobile app
Once installed, Wi-Fi cameras can be configured and managed through a web interface or mobile app provided by the manufacturer. The web interface or app allows users to customize camera settings, such as video resolution, motion detection sensitivity, and recording preferences.
Users can also set up alerts and notifications for motion events, configure remote access options, and manage user permissions. The configuration process typically involves accessing the camera’s IP address or scanning a QR code to connect to the camera’s interface.
Connecting the camera to a Wi-Fi network
To enable remote access and data transmission, Wi-Fi cameras must be connected to a Wi-Fi network. The connection process involves selecting the desired Wi-Fi network from the camera’s interface and entering the network credentials (SSID and password).
Once connected, the camera obtains an IP address from the router and establishes communication with other devices on the network. Users can then access the camera’s feed remotely using a smartphone, tablet, or computer connected to the same network or via the internet.
Data Transmission and Remote Access
Real-time streaming of video footage over Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi cameras stream live video footage over a Wi-Fi network, allowing users to monitor their property or assets in real-time. The camera captures video data, encodes it into digital format, and transmits it wirelessly to the router.
The router then forwards the data to the user’s device, such as a smartphone or computer, for viewing. Real-time streaming enables users to monitor activities and events as they occur, providing immediate awareness and response to security threats or incidents.
Remote access via smartphone, tablet, or computer
Wi-Fi cameras support remote access, allowing users to view the camera’s feed from anywhere with an internet connection. Users can access the camera’s feed using a smartphone, tablet, or computer by logging into the manufacturer’s mobile app or web interface.
Remote access features enable users to check in on their property or assets while away from home, monitor ongoing activities, and receive alerts and notifications for motion events or security breaches.
Encryption and security measures for data transmission
To ensure secure data transmission, Wi-Fi cameras implement encryption and security measures to protect against unauthorized access and interception of data. Advanced encryption protocols, such as WPA2-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 – Pre-Shared Key), encrypt data packets transmitted between the camera and the router, preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
Additionally, many Wi-Fi cameras support secure remote access via SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) encryption, which encrypts data transmitted over the internet to safeguard against interception by malicious actors.
Integration with Smart Home Systems
Compatibility with smart home platforms (e.g., Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa)
Wi-Fi cameras are often compatible with popular smart home platforms such as Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa, allowing users to integrate them into their existing smart home ecosystems. Integration with smart home platforms enables users to control and manage WiFi cameras using voice commands or through a centralized smart home hub. Users can also create custom automation routines and scenes that incorporate Wi-Fi cameras for enhanced security and convenience.
Automation and integration with other smart devices
Wi-Fi cameras can be integrated with other smart devices and sensors to create automated security systems and trigger actions based on predefined conditions. For example, users can set up motion-activated lights or sirens to deter intruders, or configure the camera to send notifications to their smartphone when motion is detected. Integration with smart home devices enhances the capabilities of WiFi cameras and provides users with greater control over their security systems.
Enhanced functionalities and features in smart home environments
In smart home environments, Wi-Fi cameras may offer additional functionalities and features tailored to home automation and integration. These features may include geofencing capabilities that automatically arm or disarm the camera based on the user’s location, or integration with smart door locks and alarms for comprehensive security solutions.
Wi-Fi cameras can also leverage smart home data and context to provide more personalized and intelligent alerts and notifications, enhancing the user experience and effectiveness of the surveillance system.
Advantages and Limitations of Wi-Fi Cameras
Advantages
- Flexibility and ease of installation: Wi-Fi cameras can be installed and configured without the need for complex wiring or professional installation, offering flexibility in placement and setup.
- Remote monitoring and accessibility: Wi-Fi cameras enable users to monitor their property or assets remotely from anywhere with an internet connection, providing peace of mind and convenience.
- Integration with smart home systems: Wi-Fi cameras seamlessly integrate with smart home platforms and devices, enabling users to create automated security systems and enhance their home automation experience.
Limitations
- Dependence on Wi-Fi network stability: Wi-Fi cameras rely on a stable Wi-Fi network for reliable data transmission, making them susceptible to disruptions or interference caused by network congestion or signal interference.
- Potential security vulnerabilities: Wi-Fi cameras may be vulnerable to cyber threats and hacking attempts if not properly secured, posing a risk to user privacy and data security.
- Limited range and signal strength: Wi-Fi cameras have a limited range and signal strength, which may affect their performance in large or obstructed environments, such as outdoor areas or multi-story buildings.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi cameras offer versatile surveillance solutions with remote access, integration with smart home systems, and easy installation. They play a significant role in modern surveillance, providing real-time monitoring and enhanced security.
Looking ahead, advancements in Wi-Fi technology and integration with emerging technologies like AI and IoT hold promise for further enhancing the capabilities and applications of Wi-Fi cameras in the future, ensuring continued effectiveness in safeguarding property and ensuring safety.
How Do Trail Cameras Work
Trail cameras are specialized devices designed for remote monitoring and surveillance in outdoor environments. These cameras are equipped with motion sensors and are typically used in wildlife observation, hunting, security, and research applications.
A trail camera consists of a camera lens and sensor, infrared (IR) emitters, a motion sensor, and a control unit with storage capabilities. They are commonly used in locations where human presence is impractical or undesirable, such as dense forests, remote trails, or private properties.
The importance of trail cameras lies in their ability to capture images or videos of wildlife, trespassers, or suspicious activities without the need for constant human supervision. Wildlife enthusiasts use trail cameras to study animal behavior, monitor populations, and contribute to conservation efforts. Hunters employ them for scouting game trails and tracking the movement patterns of target species. Additionally, trail cameras serve as a cost-effective security solution for monitoring remote areas or properties against intruders and potential threats.
Trail cameras offer a valuable tool for remote observation and data collection, with diverse applications ranging from wildlife research to security surveillance. Their versatility and ease of deployment make them indispensable for outdoor enthusiasts, researchers, and property owners alike.
Components of Trail Cameras
Trail cameras are revolutionizing the way we observe wildlife, monitor remote areas, and enhance security measures. Behind their seemingly simple exterior lies a sophisticated system of components and mechanisms that enable them to function effectively in diverse environments. In this essay, we delve deep into the intricate world of trail camera technology, exploring its components, operating mechanisms, types, and applications.
- Camera Lens and Sensor: The camera lens and sensor are fundamental components of trail cameras responsible for capturing images or videos. High-quality lenses ensure sharp and clear images, while advanced sensors determine the camera’s resolution, sensitivity, and overall image quality. Trail cameras may utilize various sensor types, including CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) and CCD (Charge-Coupled Device), each offering unique advantages in terms of image processing and low-light performance.
- Infrared (IR) Emitters: Infrared emitters are crucial for capturing images or videos in low-light conditions or complete darkness. These emitters emit invisible infrared light, illuminating the camera’s field of view without disturbing wildlife or alerting potential intruders. Trail cameras often feature infrared LEDs (Light-Emitting Diodes) arranged around the lens, providing sufficient illumination for night-time surveillance while remaining undetectable to human or animal eyes.
- Motion Sensor: The motion sensor is the trigger mechanism that activates the trail camera when movement is detected within its detection range. Most trail cameras utilize passive infrared (PIR) sensors, which detect changes in heat signatures caused by moving objects. Advanced motion sensors allow for adjustable detection ranges and sensitivity settings, enabling users to customize the camera’s response to various environmental conditions and target subjects.
- Control Unit and Storage: The control unit serves as the brain of the trail camera, managing its operation, settings, and data storage. It includes a microprocessor responsible for processing sensor inputs, controlling image capture, and managing power consumption. Trail cameras typically utilize removable memory cards, such as SD (Secure Digital) cards, to store captured images or videos. Additionally, some models may offer built-in storage options or support for cloud storage services, providing flexibility in data management and retrieval.
Operating Mechanism
- Activation Triggered by Motion or Heat: Trail cameras are designed to remain dormant until triggered by motion or heat within their detection range. When the motion sensor detects movement, it sends a signal to the control unit, prompting the camera to activate and capture images or videos. This activation mechanism conserves battery life and ensures that the camera only records relevant events, such as wildlife activity or potential security breaches.
- Detection Range and Sensitivity Adjustments: The detection range and sensitivity of trail cameras can be adjusted to optimize their performance in different environments and scenarios. Users can customize the camera’s detection range to focus on specific areas of interest and adjust sensitivity settings to avoid false triggers caused by environmental factors such as wind-blown vegetation or passing clouds. Fine-tuning these parameters allows for precise monitoring and accurate event detection.
- Day and Night Operation Modes: Trail cameras are equipped with day and night operation modes to accommodate varying light conditions. During daylight hours, the camera utilizes natural light or built-in flash units to capture color images with optimal clarity and detail. In low-light or nighttime conditions, the camera switches to infrared mode, relying on infrared emitters to illuminate the scene and capture monochrome images or videos without alerting potential subjects.
- Capturing and Storing Images or Videos: Upon activation, trail cameras capture images or videos based on user-defined settings, such as resolution, file format, and duration. Captured media files are stored locally on the camera’s memory card or internal storage, ensuring data integrity and accessibility for later retrieval. Some trail camera models may offer additional features, such as time-lapse recording or burst mode photography, to capture unique perspectives and events over extended periods.
Types of Trail Cameras
- Traditional Trail Cameras: Traditional trail cameras are standalone devices designed for manual deployment in remote locations. They rely on internal batteries or external power sources and typically require physical access to retrieve captured images or videos. Despite their simplicity, traditional trail cameras remain popular due to their reliability, affordability, and ease of use in various outdoor settings.
- Cellular Trail Cameras: Cellular trail cameras are equipped with built-in cellular modems, allowing them to transmit captured images or videos wirelessly to a designated server or mobile device. These cameras utilize cellular networks, such as 3G, 4G, or LTE, to enable remote monitoring and real-time notifications without the need for physical retrieval. Cellular trail cameras are ideal for monitoring distant or inaccessible locations and provide enhanced convenience and efficiency for users.
- Wireless Trail Cameras: Wireless trail cameras utilize wireless communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, to transfer captured images or videos to nearby devices, such as smartphones or tablets. Unlike cellular trail cameras, wireless models require proximity to the user’s device for data transmission and may have limited range or connectivity options. Wireless trail cameras offer a balance of convenience and affordability for users seeking remote monitoring capabilities without cellular network coverage.
- Specialized Trail Cameras (e.g., Time-lapse): Specialized trail cameras are designed to fulfill specific requirements or niche applications beyond standard surveillance or observation tasks. Time-lapse trail cameras, for example, capture sequential images at predetermined intervals to document changes in natural landscapes, wildlife behavior, or construction projects over extended periods. These cameras offer unique insights and creative possibilities for users interested in long-term monitoring or visual storytelling.
Trail cameras are sophisticated devices equipped with advanced components and mechanisms that enable them to operate effectively in diverse environments and scenarios. By understanding the intricacies of trail camera technology, users can harness the full potential of these devices for wildlife observation, security surveillance, and scientific research.
With ongoing advancements and innovations in trail camera technology, the possibilities for remote monitoring and data collection continue to expand, promising exciting opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts, researchers, and conservationists alike.
Factors Affecting Performance
- Battery Life and Power Source: The battery life and power source of trail cameras play a critical role in their performance and reliability. Long-lasting batteries or alternative power options, such as solar panels or external battery packs, ensure continuous operation and minimize the need for frequent maintenance or replacement. Additionally, efficient power management systems help optimize battery usage and extend operational lifespan, especially in remote or off-grid locations where access to power sources may be limited.
- Weather Resistance and Durability: Trail cameras are exposed to various weather conditions and environmental elements, making weather resistance and durability essential factors affecting their performance. Robust construction materials, such as weatherproof housing and seals, protect trail cameras from moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures, ensuring reliable operation in harsh outdoor environments. Furthermore, rugged design features, including shock resistance and tamper-proof enclosures, enhance durability and longevity, minimizing the risk of damage or malfunction due to environmental hazards or physical impact.
- Image Quality and Resolution: The image quality and resolution of trail camera footage directly impact their effectiveness in capturing clear and detailed images or videos. High-resolution cameras with advanced image processing capabilities produce sharp and vivid imagery, enabling accurate identification and analysis of subjects, such as wildlife species or intruders. Additionally, adjustable settings for image resolution and compression allow users to balance image clarity with storage space requirements, optimizing performance for specific monitoring objectives and scenarios.
- Trigger Speed and Recovery Time: Trigger speed and recovery time are crucial performance metrics that determine the responsiveness and efficiency of trail cameras in capturing fast-moving subjects or consecutive events. Fast trigger speeds ensure minimal delay between motion detection and image capture, reducing the risk of missed opportunities or motion blur in dynamic environments. Similarly, rapid recovery times enable trail cameras to reset quickly after capturing an image or video, allowing for continuous monitoring and capturing of subsequent events without interruption.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Remote Monitoring and Surveillance: Trail cameras enable remote monitoring and surveillance of wildlife habitats, remote trails, or property perimeters without the need for direct human presence, providing valuable insights and real-time alerts for monitoring and management purposes.
- Wildlife Research and Observation: Trail cameras facilitate non-invasive wildlife research and observation by capturing natural behaviors and interactions in their natural habitats, contributing to scientific studies, conservation efforts, and environmental education initiatives.
- Security and Property Protection: Trail cameras serve as cost-effective and versatile security solutions for monitoring and protecting remote or vulnerable areas, deterring trespassers, vandals, or wildlife intruders, and providing evidence for law enforcement or insurance purposes.
Limitations
- Limited Battery Life in Remote Areas: Trail cameras operating in remote or off-grid locations may experience limited battery life due to prolonged usage or insufficient sunlight for solar charging, requiring frequent battery replacements or alternative power solutions to maintain continuous operation.
- Vulnerable to Theft or Damage: Trail cameras are susceptible to theft or damage when deployed in unprotected or accessible locations, posing a risk of loss or compromise of valuable equipment and data, necessitating secure mounting options and anti-theft measures to mitigate security risks.
- Potential for False Triggers: Trail cameras may experience false triggers caused by environmental factors, such as wind-blown vegetation, moving shadows, or small animals, resulting in unnecessary image or video capture and increased data storage requirements, requiring careful placement and sensitivity adjustments to minimize false alarms.
Applications of Trail Cameras
- Wildlife Management and Conservation: Trail cameras are widely used in wildlife management and conservation initiatives to monitor populations, track movements, and study behaviors of various species, providing valuable data for habitat management, population assessments, and conservation planning efforts.
- Hunting and Scouting: Hunters utilize trail cameras for scouting game trails, monitoring feeding areas, and assessing target species’ activity patterns, enhancing hunting success rates and minimizing disturbance to wildlife populations through informed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Home Security and Surveillance: Trail cameras serve as effective home security and surveillance solutions for monitoring residential properties, detecting intruders or suspicious activities, and providing visual evidence for law enforcement or insurance claims, offering homeowners peace of mind and enhanced protection against potential threats.
- Research and Scientific Studies: Trail cameras are instrumental in research and scientific studies across various disciplines, including ecology, biology, and environmental science, enabling researchers to monitor ecosystems, study species interactions, and investigate ecological phenomena in remote or inaccessible locations, advancing scientific knowledge and informing conservation strategies.
Future Trends and Innovations
- Advancements in Sensor Technology: Ongoing advancements in sensor technology, such as improved image sensors and motion detection algorithms, are enhancing trail camera performance, enabling higher resolution imagery, faster trigger speeds, and more accurate event detection capabilities, enhancing overall monitoring and surveillance effectiveness.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence for Image Analysis: Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms is revolutionizing trail camera technology, enabling automated image analysis, species recognition, and behavior classification, streamlining data processing and interpretation for researchers and conservationists, and unlocking new insights into wildlife ecology and behavior.
- Enhanced Connectivity Options: Trail cameras are adopting enhanced connectivity options, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth capabilities, facilitating real-time data transmission, remote control, and cloud-based storage solutions, enabling seamless integration with mobile devices and web-based platforms for enhanced user experience and accessibility.
- Development of Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Models: Increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability is driving the development of eco-friendly and sustainable trail camera models, incorporating energy-efficient designs, recyclable materials, and renewable power sources, reducing environmental impact and promoting responsible outdoor monitoring practices.
Conclusion
Trail cameras are versatile and powerful tools for remote monitoring, surveillance, and research applications, offering numerous advantages in wildlife management, hunting, security, and scientific studies. However, their performance is influenced by various factors, including battery life, weather resistance, image quality, and trigger speed, as well as limitations such as susceptibility to theft or false triggers.
As trail camera technology continues to evolve, future trends and innovations hold promising prospects for advancing monitoring capabilities, enhancing connectivity options, and promoting environmental sustainability, shaping the future of outdoor surveillance and conservation efforts.
How Do Nanny Cameras Work?
Nanny cameras, often referred to as childcare cameras or babysitter cams, are discreet surveillance devices used to monitor caregivers’ interactions with children, elders, or pets in a home environment. These cameras are typically small and inconspicuous, allowing them to be placed in various locations throughout the home without detection.
The importance of nanny cameras lies in their role as a tool for ensuring the safety, well-being, and security of those under the care of others. Parents and guardians can use nanny cameras to observe and assess the quality of care provided by babysitters, nannies, or caregivers while they are away from home. This surveillance technology offers peace of mind by allowing parents to remotely monitor their children’s activities, ensure they are being treated with kindness and respect, and detect any potential signs of neglect or abuse.
Beyond childcare monitoring, nanny cameras have a range of applications, including supervising elder care, pet sitting, housekeeping, and enhancing home security. They serve as a proactive measure to protect vulnerable individuals and property, provide evidence in case of disputes or incidents, and promote accountability and transparency in caregiving arrangements.
Nanny cameras play a crucial role in safeguarding the welfare of those entrusted to the care of others, offering reassurance and security to families and caregivers alike.
Components of Nanny Cameras
- Camera Lens and Sensor: The camera lens and sensor are essential components of nanny cameras responsible for capturing images or videos. High-quality lenses ensure clear and detailed footage, while advanced sensors determine the camera’s resolution, sensitivity, and low-light performance. Nanny cameras may utilize CMOS or CCD sensors, each offering unique advantages in terms of image quality and processing capabilities.
- Infrared (IR) Emitters: Infrared emitters are crucial for capturing footage in low-light conditions or complete darkness. These emitters emit invisible infrared light, illuminating the camera’s field of view without alerting caregivers or intruders. Nanny cameras often feature infrared LEDs arranged around the lens, providing sufficient illumination for nighttime surveillance while remaining discreet and unobtrusive.
- Motion Sensor: The motion sensor is a key component of nanny cameras that detects movement within its detection range. Passive infrared (PIR) sensors are commonly used to detect changes in heat signatures caused by moving objects, triggering the camera to start recording. Adjustable sensitivity settings allow users to customize the camera’s response to motion, minimizing false alarms and conserving storage space.
- Control Unit and Storage: The control unit serves as the brain of the nanny camera, managing its operation, settings, and data storage. It includes a microprocessor responsible for processing sensor inputs, controlling recording functions, and managing power consumption. Nanny cameras typically utilize onboard storage, such as SD cards, to store captured images or videos, providing convenient access to recorded footage for review or playback.
Operating Mechanism
- Activation Triggered by Motion or Sound: Nanny cameras are activated by motion or sound within their detection range, prompting them to start recording. When the motion sensor detects movement or the sound sensor detects noise, the camera is triggered to capture footage of the event. This activation mechanism ensures that the camera only records relevant activity, conserving storage space and battery life.
- Detection Range and Sensitivity Adjustments: Users can adjust the detection range and sensitivity of nanny cameras to optimize their performance in different environments. By customizing these settings, users can focus the camera’s attention on specific areas of interest and fine-tune its response to motion or sound, reducing the likelihood of false alarms or missed events.
- Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities: Some nanny cameras offer real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing users to remotely view live footage from their smartphone, tablet, or computer. Wi-Fi-enabled nanny cameras can connect to a home network, providing instant access to live video streams and alerts via a dedicated mobile app or web interface.
- Capturing and Storing Images or Videos: Upon activation, nanny cameras capture images or videos based on user-defined settings, such as resolution, frame rate, and recording duration. Captured media files are stored locally on the camera’s onboard storage or transmitted to a connected device or cloud storage service for safekeeping. This allows users to review, share, or archive recorded footage as needed.
Types of Nanny Cameras
- Hidden Nanny Cameras: Hidden nanny cameras are designed to be discreetly concealed within everyday objects, such as alarm clocks, smoke detectors, or picture frames. These covert cameras blend seamlessly into their surroundings, allowing caregivers to monitor activities without arousing suspicion or discomfort.
- Wi-Fi-Enabled Nanny Cameras: Wi-Fi-enabled nanny cameras connect to a home network, allowing users to access live video feeds and recordings remotely via a smartphone, tablet, or computer. These cameras offer enhanced convenience and flexibility, enabling caregivers to monitor their home and loved ones from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Battery-Powered Nanny Cameras: Battery-powered nanny cameras are portable and versatile, making them ideal for temporary surveillance or locations without access to electrical outlets. These cameras rely on rechargeable batteries for power, providing flexibility in placement and installation without the need for wiring or external power sources.
- Nanny Cameras with Built-In DVR: Nanny cameras with built-in DVR (Digital Video Recorder) functionality offer onboard storage for recording and storing footage directly on the camera itself. These cameras eliminate the need for external storage devices or cloud subscriptions, providing a convenient and cost-effective solution for capturing and accessing recorded footage.
Factors Affecting Performance
- Battery Life and Power Source: The battery life and power source of nanny cameras influence their performance and reliability, especially in remote or off-grid locations. Long-lasting batteries or alternative power options, such as solar panels or external battery packs, ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime due to power issues.
- Video Quality and Resolution: The video quality and resolution of nanny camera footage impact its clarity and detail, affecting the ability to identify individuals or events accurately. High-resolution cameras with advanced image processing capabilities produce sharp and vivid imagery, providing clear evidence in case of disputes or incidents.
- Field of View and Angle Adjustment: The field of view and angle adjustment of nanny cameras determine the coverage area and perspective captured by the camera. Wide-angle lenses offer broader coverage, allowing users to monitor larger areas with fewer cameras, while adjustable mounts or swivel mechanisms enable users to customize the camera’s viewing angle for optimal placement and coverage.
- Connectivity Options and Remote Access: The connectivity options and remote access capabilities of nanny cameras influence their accessibility and usability. Wi-Fi-enabled cameras offer seamless integration with home networks, enabling remote monitoring and control via mobile apps or web interfaces. Additionally, cloud storage services provide convenient access to recorded footage and alerts, ensuring data is securely backed up and accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Legal Considerations and Privacy Issues
- Legal Regulations Regarding Surveillance in Private Spaces: The use of nanny cameras is subject to legal regulations governing surveillance in private spaces, which vary depending on jurisdiction. In many regions, individuals have the right to install surveillance cameras within their own homes for security and safety purposes. However, laws typically prohibit the recording of audio without consent and may impose restrictions on the placement of cameras in areas where individuals have a reasonable expectation of privacy, such as bathrooms or bedrooms.
- Consent and Notification Requirements: Consent and notification requirements for the use of nanny cameras vary by location and may be influenced by state or local laws. In some jurisdictions, caregivers must provide consent or be informed of the presence of surveillance cameras in areas where they work. Failure to comply with consent or notification requirements can result in legal consequences, including civil liability for invasion of privacy or violation of wiretapping laws.
- Ethical Implications of Using Nanny Cameras: The use of nanny cameras raises ethical concerns regarding privacy, trust, and autonomy. Caregivers may feel violated or mistrusted if they discover they are being monitored without their knowledge or consent. Additionally, the constant surveillance of caregivers may create a culture of surveillance and undermine the development of trusting relationships between caregivers and families.
- Safeguards Against Misuse and Abuse: To mitigate the risks of misuse and abuse associated with nanny cameras, it is essential to establish clear guidelines and safeguards for their use. This may include obtaining consent from caregivers, providing notice of surveillance, and implementing secure data storage practices to protect the privacy and confidentiality of recorded footage.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Monitoring Child or Elder Care Remotely: Nanny cameras allow parents and caregivers to monitor the well-being and safety of children or elders from anywhere with an internet connection, providing reassurance and peace of mind.
- Ensuring Safety and Security in the Home: Nanny cameras serve as a proactive measure to deter intruders, prevent theft or vandalism, and enhance home security by providing visual evidence of suspicious activity.
- Providing Peace of Mind for Parents and Caregivers: The use of nanny cameras offers parents and caregivers peace of mind by allowing them to monitor their loved ones’ activities and interactions, even when they are not physically present.
Limitations
- Invasion of Privacy Concerns: Nanny cameras raise concerns about the invasion of privacy, particularly for caregivers who may feel uncomfortable or surveilled without their knowledge or consent.
- Vulnerability to Hacking or Unauthorized Access: Nanny cameras connected to the internet are susceptible to hacking or unauthorized access, potentially compromising the privacy and security of recorded footage.
- Potential for False Alarms or Misinterpretation of Footage: Nanny cameras may trigger false alarms or misinterpretations of footage due to technical glitches, environmental factors, or human error, leading to unnecessary stress or confusion for caregivers and families.
Applications of Nanny Cameras
- Monitoring Childcare Providers or Babysitters: Nanny cameras are commonly used to monitor childcare providers, such as babysitters or nannies, to ensure they are providing attentive and responsible care to children in their charge.
- Supervising Elder Care or Home Caregivers: Nanny cameras can be used to supervise elder care or home caregivers, allowing family members to monitor the well-being and safety of elderly or disabled individuals receiving in-home care.
- Preventing Theft or Vandalism in the Home: Nanny cameras serve as a deterrent to theft or vandalism in the home by providing surveillance coverage of entry points, valuable possessions, or common areas where intruders may attempt to gain access.
- Recording Evidence of Wrongdoing or Abuse: Nanny cameras can record evidence of wrongdoing or abuse, such as neglect, mistreatment, or theft, providing valuable documentation for legal proceedings or disciplinary actions.
Future Trends and Innovations
- Integration with Smart Home Technology: Nanny cameras are increasingly integrated with smart home technology, allowing for seamless integration with other devices and systems, such as home security systems, voice assistants, and mobile apps.
- Enhanced Video Analytics and Facial Recognition: Future nanny cameras may incorporate advanced video analytics and facial recognition technology to identify individuals, detect suspicious activity, and provide personalized alerts and notifications.
- Improved Privacy Features and Data Security Measures: Manufacturers are focusing on improving privacy features and data security measures to protect against hacking, unauthorized access, and misuse of recorded footage, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of recorded data.
- Development of More Discreet and Covert Designs: Nanny cameras may evolve to include more discreet and covert designs, allowing them to blend seamlessly into home environments and minimize the risk of detection or tampering by caregivers or intruders.
Conclusion
Nanny cameras offer valuable advantages in monitoring childcare, elder care, and home security, but they also raise important legal considerations, privacy issues, and ethical concerns. By understanding the advantages, limitations, and potential applications of nanny cameras, caregivers and families can make informed decisions about their use and implementation, ensuring the safety, security, and well-being of their loved ones in the home environment.
Home Security Cameras and Privacy: What You Need To
Home security cameras have become an integral part of modern surveillance systems, offering homeowners peace of mind and a sense of security. However, as the use of these cameras becomes more widespread, so do concerns about privacy implications. This essay explores the intersection of home security cameras and privacy concerns, aiming to shed light on the challenges and considerations involved in maintaining a balance between security and privacy.
Home security cameras are electronic devices designed to monitor and record activities in and around residential properties. They come in various forms, including indoor and outdoor cameras, as well as wired and wireless options. These cameras typically feature motion detection, night vision, and remote access capabilities, allowing homeowners to monitor their property from anywhere via smartphone apps or web portals.
With the increasing prevalence of home security cameras, there has been a corresponding rise in concerns about privacy implications. These concerns stem from the potential for invasion of privacy, as well as legal and ethical considerations surrounding surveillance in residential areas. As cameras become more advanced and ubiquitous, it becomes essential to examine how they impact individuals’ privacy rights and freedoms.
The purpose of this topic outline is to delve into the multifaceted relationship between home security cameras and privacy concerns. By exploring the different types of cameras, their features, and their importance in crime prevention, as well as the privacy risks they pose and the strategies for mitigating these risks, this essay aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the complex issues at play.
Home Security Cameras
- Types of Home Security Cameras: There are several types of home security cameras available on the market, each with its own set of features and functionalities. Indoor cameras are typically used to monitor the interior of a home, while outdoor cameras are designed to withstand the elements and provide surveillance of outdoor spaces. Wired cameras require a physical connection to a power source and often a recording device, while wireless cameras operate via Wi-Fi and are easier to install and relocate.
- Common Features and Functionalities: Common features found in home security cameras include motion detection, night vision, two-way audio, and cloud storage for recorded footage. These features allow homeowners to monitor their property in real-time, receive alerts of suspicious activity, and review recorded footage as needed.
- Importance of Home Security Cameras in Crime Prevention and Monitoring: Home security cameras play a vital role in deterring crime and providing evidence in the event of a security breach. Studies have shown that the presence of visible security cameras can significantly reduce the likelihood of burglary and other property crimes. Additionally, cameras can help homeowners monitor the activities of visitors, delivery personnel, and potential intruders, enhancing overall security and peace of mind.
Privacy Concerns with Home Security Cameras
- Invasion of Privacy: Potential Risks and Implications: One of the primary concerns surrounding home security cameras is the potential for invasion of privacy. Cameras installed in and around residential properties may inadvertently capture the activities of neighbors, passersby, and other individuals who have not consented to being recorded. This raises questions about the appropriate use of surveillance technology and the rights of individuals to privacy in their own homes.
- Legal Considerations and Regulations Regarding Surveillance in Residential Areas: The use of home security cameras is subject to various legal considerations and regulations, which may vary depending on jurisdiction. In many regions, homeowners are required to obtain consent from individuals before recording them on private property. Additionally, there may be restrictions on where cameras can be installed and how footage can be used or shared.
- Ethical Considerations Related to the Use of Home Security Cameras: Beyond legal requirements, there are ethical considerations to take into account when deploying home security cameras. These include considerations of fairness, consent, and respect for individuals’ privacy rights. Homeowners must weigh the benefits of surveillance for security purposes against the potential intrusions on privacy and the broader societal implications of widespread surveillance.
Balancing Security and Privacy
- Strategies for Minimizing Privacy Risks While Maximizing Security Benefits: Finding the right balance between security and privacy requires careful consideration and planning. Homeowners can implement various strategies to minimize privacy risks while still reaping the benefits of home security cameras. This may include adjusting camera angles and settings to avoid capturing sensitive areas, such as neighboring properties or public spaces, and using privacy-enhancing features such as masking or blurring certain areas of recorded footage.
- Importance of Transparency and Consent in Deploying Home Security Cameras: Transparency and consent are essential principles in the deployment of home security cameras. Homeowners should inform neighbors and visitors about the presence of cameras on their property and obtain consent from individuals before recording them. Clear signage indicating the use of surveillance cameras can help communicate expectations and respect individuals’ privacy rights.
Implementing Privacy-Enhancing Features and Practices in Camera Systems
Many modern home security cameras offer privacy-enhancing features and practices that allow homeowners to maintain a balance between security and privacy. These features may include customizable motion detection zones, privacy masking, and encryption of recorded footage. By leveraging these features and adopting best practices for camera deployment and usage, homeowners can enhance privacy protections while still benefiting from the security provided by surveillance technology.
The intersection of home security cameras and privacy concerns presents a complex and multifaceted issue. By understanding the different types of cameras, their features, and their importance in crime prevention, as well as the privacy risks they pose and the strategies for mitigating these risks, homeowners can make informed decisions about the deployment and usage of surveillance technology.
By prioritizing transparency, consent, and privacy-enhancing practices, homeowners can strike a balance between security and privacy, ensuring the protection of their property and the rights of individuals in their community.
Ensuring the security of home security camera systems is crucial for protecting privacy and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive footage and data. This section explores best practices for securing camera systems, emphasizing the importance of regular updates and safeguarding collected data.
- Best Practices for Securing Camera Systems Against Unauthorized Access: Securing home security camera systems begins with implementing robust access controls. This includes using strong, unique passwords for camera accounts and enabling two-factor authentication where available. Additionally, homeowners should regularly review and update access permissions to limit who can view and control the cameras.
- Importance of Regularly Updating Firmware and Software: Regularly updating firmware and software is essential for addressing security vulnerabilities and ensuring the continued reliability and performance of home security camera systems. Manufacturers often release updates to patch known security flaws and improve system stability. Homeowners should enable automatic updates whenever possible and stay informed about new releases and patches through manufacturer notifications.
- Tips for Safeguarding Footage and Data Collected by Home Security Cameras: Safeguarding footage and data collected by home security cameras is essential for protecting privacy and preventing unauthorized access. Homeowners should ensure that recorded footage is encrypted during transmission and storage to prevent interception by malicious actors. Additionally, storing footage locally on secure devices or encrypted cloud servers can help mitigate the risk of data breaches.
User Education and Awareness
Educating users about privacy-conscious camera usage and promoting responsible and ethical use of surveillance technology is essential for fostering a culture of privacy awareness. This section explores resources and guidance for homeowners, as well as the potential risks and benefits of home security cameras.
- Providing Resources and Guidance for Homeowners on Privacy-Conscious Camera Usage: Homeowners should have access to resources and guidance on how to deploy and configure home security cameras in a privacy-conscious manner. This includes information on how to adjust camera settings to minimize privacy risks, as well as guidance on legal and ethical considerations related to surveillance in residential areas.
- Educating Users about the Potential Risks and Benefits of Home Security Cameras: Educating users about the potential risks and benefits of home security cameras is essential for fostering informed decision-making. Homeowners should be aware of the privacy implications of deploying surveillance technology on their property, as well as the potential benefits in terms of crime prevention and monitoring.
- Promoting Responsible and Ethical Use of Surveillance Technology: Promoting responsible and ethical use of surveillance technology involves encouraging homeowners to consider the broader societal implications of deploying home security cameras. This includes respecting the privacy rights of neighbors and passersby, obtaining consent before recording individuals on private property, and being transparent about the presence of surveillance cameras.
Case Studies and Examples
Examining real-world examples of privacy incidents related to home security cameras, as well as successful implementations of privacy-conscious camera systems, can provide valuable insights and lessons learned for homeowners and manufacturers alike.
- Real-World Examples of Privacy Incidents Related to Home Security Cameras: Real-world examples of privacy incidents related to home security cameras highlight the potential risks and consequences of inadequate security measures. This may include instances of unauthorized access to camera feeds, data breaches resulting in the exposure of sensitive footage, or legal disputes arising from privacy violations.
- Successful Implementations of Privacy-Conscious Camera Systems: Successful implementations of privacy-conscious camera systems demonstrate that it is possible to strike a balance between security and privacy. These examples showcase innovative solutions and best practices for securing camera systems against unauthorized access and protecting the privacy of individuals in residential areas.
- Lessons Learned and Best Practices from Case Studies: Examining case studies and examples provides valuable lessons learned and best practices for homeowners and manufacturers to consider when deploying and managing home security camera systems. This may include recommendations for securing camera systems, mitigating privacy risks, and fostering a culture of privacy awareness among users.
Future Trends and Considerations
Exploring emerging technologies and their impact on home security and privacy, as well as predictions for the evolution of privacy regulations and industry standards, can help stakeholders stay ahead of privacy challenges and anticipate future trends.
- Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Home Security and Privacy: Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, facial recognition, and smart home integration are reshaping the landscape of home security and privacy. These technologies offer new opportunities for enhanced security and convenience but also raise concerns about privacy implications and potential abuses.
- Predictions for the Evolution of Privacy Regulations and Industry Standards: Predictions for the evolution of privacy regulations and industry standards can help stakeholders anticipate future challenges and adapt their practices accordingly. As privacy concerns continue to garner attention from policymakers and the public alike, it is likely that we will see increased regulation and scrutiny of surveillance technology in the coming years.
- Recommendations for Homeowners and Manufacturers to Stay Ahead of Privacy Challenges: To stay ahead of privacy challenges, homeowners and manufacturers should prioritize privacy in the design, deployment, and use of home security camera systems. This may include implementing privacy-enhancing features and practices, staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities, and actively engaging with policymakers and industry stakeholders to shape the future of privacy regulation.
Conclusion
Addressing privacy concerns in home security camera systems requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses technical, legal, and ethical considerations. By implementing best practices for securing camera systems, educating users about privacy-conscious usage, learning from real-world examples and case studies, and anticipating future trends and challenges, stakeholders can work together to foster a culture of privacy awareness and responsibility in the deployment and use of home security cameras.
Do Security Cameras Record All the Time
Security cameras have become a ubiquitous feature in modern society, serving as essential tools for monitoring and protecting property, people, and assets. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the world of security cameras, starting with a definition of their purpose and an overview of the topic: Do security cameras record all the time?
Security cameras, also known as surveillance cameras or closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras, are electronic devices equipped with sensors and lenses to capture video footage of a specific area or location. These cameras are commonly used in various settings, including homes, businesses, public spaces, and government facilities, to deter crime, enhance safety, and provide valuable evidence in the event of security incidents.
The question of whether security cameras record all the time is a fundamental aspect of surveillance system operation and management. While the answer may vary depending on various factors, including camera type, settings, and surveillance objectives, understanding the capabilities and limitations of security cameras is essential for effective security planning and implementation.
Understanding Security Cameras
Types of Security Cameras
- Analog vs. IP Cameras: Analog cameras transmit video signals over coaxial cables to recording devices such as DVRs. In contrast, IP (Internet Protocol) cameras digitize video footage and transmit it over computer networks, offering higher resolution and advanced features such as remote access and analytics.
- Fixed vs. PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) Cameras: Fixed cameras have a stationary field of view and capture footage from a fixed position, while PTZ cameras can pan, tilt, and zoom to cover a wider area and provide flexible surveillance coverage.
Functionality of Security Cameras
- Continuous Recording vs. Motion-Activated Recording: Security cameras can be configured to record continuously, capturing video footage around the clock, or activated by motion sensors to record only when motion is detected, conserving storage space and reducing the need for manual review.
- Storage Options: Local Storage vs. Cloud Storage: Recorded video footage can be stored locally on physical devices such as DVRs or NVRs or uploaded to cloud-based storage services for remote access and backup. Each storage option offers unique benefits and considerations in terms of accessibility, scalability, and data security.
Factors Affecting Recording
Camera Settings and Configurations
- Recording Modes and Schedules: Security cameras can be programmed to operate in different recording modes, such as continuous recording, scheduled recording at specific times, or event-triggered recording based on motion detection or other sensor inputs.
- Motion Detection Sensitivity: Adjusting motion detection sensitivity allows users to customize camera behavior and minimize false alarms triggered by irrelevant motion, such as moving foliage or passing vehicles.
Surveillance System Capabilities
- DVR vs. NVR: DVRs and NVRs are recording devices that capture and store video footage from connected cameras. DVRs are designed for analog cameras, while NVRs are compatible with IP cameras and offer advanced features such as remote access and video analytics.
- Camera Resolution and Frame Rate: Higher camera resolution and frame rates result in clearer, smoother video footage but also require more storage space and bandwidth. Surveillance system capabilities, including storage capacity and network bandwidth, must accommodate the recording requirements of the installed cameras.
Legal and Privacy Considerations
Surveillance Laws and Regulations
- Consent Requirements: Surveillance laws and regulations vary by jurisdiction but generally require businesses and organizations to inform individuals about the presence of security cameras and obtain their consent to record video footage in certain settings, such as workplaces or public areas.
- Privacy Rights: Individuals have privacy rights regarding the collection, storage, and use of their personal data, including video footage captured by security cameras. Compliance with privacy laws and regulations is essential to protect the rights and privacy of individuals under surveillance.
Security Camera Policies
- Workplace Surveillance Policies: Employers may implement surveillance policies to monitor employee activities in the workplace for security, safety, or productivity purposes. These policies should be transparent, fair, and compliant with applicable laws and regulations governing workplace surveillance.
- Residential Surveillance Policies: Homeowners and residents may install security cameras to protect their property and enhance home security. However, considerations such as camera placement, privacy implications, and compliance with local regulations should be addressed to respect the privacy rights of neighbors and passersby.
Security cameras play a crucial role in enhancing safety, protecting property, and deterring crime in various settings. Understanding the functionality, types, and legal considerations of security cameras is essential for deploying effective surveillance systems that balance security needs with privacy rights and legal compliance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Continuous recording is a fundamental aspect of surveillance systems, offering both advantages and disadvantages that impact their effectiveness and ethical considerations.
Advantages of Continuous Recording
Comprehensive Surveillance Coverage: One of the primary advantages of continuous recording is its ability to provide comprehensive surveillance coverage. By capturing every moment within the camera’s field of view, continuous recording ensures that no events or incidents go unnoticed.
This comprehensive coverage is essential for monitoring large areas, high-risk zones, or critical assets where constant vigilance is required. Whether it’s monitoring a busy intersection, a crowded public space, or a sensitive facility, continuous recording offers peace of mind by ensuring that all activities are captured and recorded for review.
Documentation of Events in Real-Time: Continuous recording enables real-time documentation of events as they unfold, offering valuable insights into security incidents, emergencies, or suspicious activities. Security personnel have immediate access to live footage, allowing them to respond promptly to security breaches, assess situations accurately, and initiate appropriate interventions.
Whether it’s detecting unauthorized access, responding to emergencies, or preventing potential threats, continuous recording provides security teams with the information they need to act decisively and effectively. This real-time documentation enhances situational awareness, facilitates rapid response, and minimizes the impact of security incidents.
Disadvantages of Continuous Recording
Increased Storage Requirements: Despite its benefits, continuous recording imposes significant storage requirements, especially when high-resolution cameras are used or when recording multiple camera feeds simultaneously.
The continuous accumulation of video data consumes vast amounts of storage space, leading to higher storage costs and the need for regular maintenance and management of storage systems. Managing large volumes of recorded footage poses logistical challenges, including storage capacity planning, data retention policies, and data backup strategies.
Additionally, the scalability of storage infrastructure becomes a concern as surveillance systems expand or upgrade to accommodate additional cameras or higher resolutions.
Privacy Concerns and Ethical Implications: Continuous recording raises privacy concerns and ethical implications, as it may capture sensitive or private information about individuals within the surveillance area. The indiscriminate recording of people’s activities without their consent or knowledge infringes on their privacy rights and may lead to unauthorized surveillance or surveillance abuse.
There is a risk of unauthorized access to recorded footage, potential misuse of personal data, and unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information. Moreover, the prolonged retention of recorded footage increases the likelihood of privacy breaches or data breaches, exposing individuals to potential harm or exploitation. To address these concerns, organizations must implement robust privacy policies, access controls, and data protection measures to safeguard the privacy and security of individuals captured by surveillance cameras.
Continuous recording offers comprehensive surveillance coverage and real-time documentation of events, but it also presents challenges such as increased storage requirements and privacy concerns. Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of continuous recording requires careful consideration of operational needs, technical capabilities, and ethical considerations. By implementing appropriate storage solutions, privacy safeguards, and ethical guidelines, organizations can harness the benefits of continuous recording while minimizing its potential drawbacks and ensuring responsible and ethical use of surveillance technology.
Alternatives and Solutions
Motion-Activated Recording
Motion-activated recording serves as an efficient alternative to continuous recording, offering solutions to the challenges of storage usage while prioritizing the capture of significant events.
- Reduction of Storage Usage: The essence of motion-activated recording lies in its ability to conserve storage space by activating recording only when motion is detected within the camera’s field of view. Unlike continuous recording, which captures every moment, regardless of activity, motion-activated recording focuses solely on events that trigger motion sensors. This selective approach significantly reduces the volume of data stored, minimizing storage costs and alleviating the burden on storage systems.
- Focus on Significant Events: By capturing only events where motion is detected, motion-activated recording ensures that security personnel can quickly identify and review relevant footage without the need to sift through hours of continuous recording. This focus on significant events enables security teams to prioritize their attention on potential security breaches, intrusions, movements, or other suspicious activities captured by the cameras. As a result, valuable time and resources are saved, and security responses can be swift and targeted.
Scheduled Recording
Scheduled recording provides a flexible approach to surveillance recording, allowing organizations to balance surveillance needs with resource constraints while optimizing storage usage and system performance.
- Balancing Surveillance Needs with Resource Constraints: Scheduled recording empowers users to define specific time periods for recording based on surveillance priorities, operational hours, or security requirements. Organizations can customize recording schedules to align with peak activity periods, high-risk hours, or specific events of interest. By tailoring recording schedules to match surveillance objectives, organizations can allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that surveillance systems operate effectively without unnecessary recording during periods of low activity.
- Optimizing Storage Usage and System Performance: By recording during predetermined time periods or when security risks are highest, scheduled recording optimizes storage usage and system performance. Rather than continuously recording footage around the clock, scheduled recording conserves storage space by capturing only the most relevant and actionable footage.
This proactive approach helps prevent storage overloads, reduces storage costs, and ensures that surveillance systems operate smoothly and reliably. Additionally, scheduled recording allows organizations to prioritize critical areas or assets for surveillance, directing resources where they are most needed while maintaining overall system efficiency.
Best Practices for Security Camera Usage
Clear Communication and Signage
- Notifying Individuals of Surveillance Presence: Transparent communication and clear signage should be employed to inform individuals of the presence of security cameras and their purpose for recording. Proper signage alerts individuals to the potential recording of their actions, promoting transparency and compliance with privacy regulations. By openly acknowledging the use of surveillance cameras, organizations foster trust and respect for individuals’ privacy rights while enhancing security measures.
- Establishing Expectations for Recording Practices: Organizations should establish clear expectations for recording practices, including the purpose of surveillance, the retention period of recorded footage, and individuals’ rights regarding access to their personal data. By outlining these guidelines and policies, organizations can mitigate privacy concerns and build trust with stakeholders. Transparent communication fosters accountability and ensures that surveillance practices align with ethical standards and legal requirements.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
- Ensuring Cameras are Operational: Regular maintenance and monitoring of security cameras are essential to ensure that cameras are operational, properly aligned, and free from obstructions. Routine checks should be conducted to verify camera functionality, assess image quality, and address any technical issues promptly. By maintaining surveillance equipment in optimal condition, organizations can maximize the effectiveness of their security systems and ensure that critical events are captured accurately.
- Reviewing Footage for Security Purposes: Security personnel should routinely review recorded footage for security purposes, including investigating security incidents, identifying potential threats, and gathering evidence for law enforcement purposes. Timely review and analysis of footage enhance security measures and facilitate proactive response to security threats. By regularly monitoring recorded footage, organizations can detect suspicious activities, prevent security breaches, and maintain a safe and secure environment for all stakeholders.
Motion-activated recording and scheduled recording offer practical solutions to the challenges of surveillance recording, balancing surveillance needs with resource constraints while optimizing storage usage and system performance. Clear communication, regular maintenance, and proactive monitoring are essential best practices for ensuring the effective and ethical use of security cameras, promoting transparency, accountability, and privacy protection. By implementing these practices, organizations can enhance security measures, mitigate privacy risks, and foster trust and confidence among stakeholders.
Conclusion
Continuous recording offers comprehensive surveillance coverage and real-time documentation of events but presents challenges such as increased storage requirements and privacy concerns. Alternatives such as motion-activated recording and scheduled recording address these challenges by reducing storage usage, focusing on significant events, and optimizing system performance.
Best practices for security camera usage include clear communication and signage, regular maintenance and monitoring, and responsible handling of recorded footage. By implementing these practices, organizations can enhance security measures, mitigate privacy risks, and ensure the effective operation of surveillance systems.
Do Ring Cameras Record 24/7?
Yes… But You Need A Few Things…
Most Ring Cameras Need Other Equipment And Subscriptions To Record 24/7
Here Is What You Need:
- Ring Alarm Pro Base Station: Necessary for 24/7 recording on Ring cameras. Approx. $250.
- Hard Drive for Ring Alarm Pro: Needed for local storage. Approx. $50.Ring cameras represent a significant advancement in home security technology, offering homeowners a comprehensive surveillance solution. These devices, developed by Ring, provide users with real-time video monitoring, two-way audio communication, and motion detection capabilities.
The importance of home security systems cannot be overstated in today’s world, where burglary and property crimes are unfortunately common occurrences. Ring cameras offer a sense of peace and security, allowing homeowners to monitor their property remotely and receive instant alerts about suspicious activities.
24/7 Recording Cameras Via Security Systems
Vivint 24/7 Recording
Vivint offers comprehensive home security solutions, including 24/7 recording capabilities through its security cameras and DVR/NVR systems. Here’s how Vivint supports 24/7 recording:
- Smart Drive: Vivint’s Smart Drive allows for continuous recording. It stores video footage locally, providing up to 30 days of continuous recording. The Smart Drive integrates with Vivint’s indoor, outdoor, and doorbell cameras.
- Cloud Storage: Vivint cameras come with cloud storage options, which store video clips when motion is detected or an event is triggered. Continuous cloud recording is typically achieved through additional storage plans.
- Camera Integration: Vivint’s security cameras are designed to integrate seamlessly with their Smart Home system. This includes indoor cameras, outdoor cameras, and doorbell cameras, all of which can be configured for continuous recording.
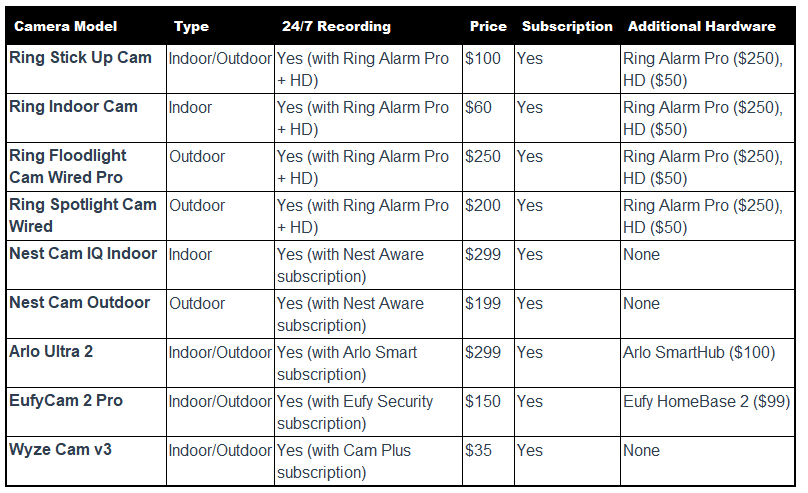
Pricing Comparison Table
Here’s a comparison table for Vivint’s 24/7 recording options against other security camera systems that offer 24/7 recording:
| Camera/System | Type | 24/7 Recording Support | Price (Approx.) | Subscription Required | Additional Hardware Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vivint Indoor Camera | Indoor | Yes (with Smart Drive) | $199 | Yes | Vivint Smart Drive ($249) |
| Vivint Outdoor Camera Pro | Outdoor | Yes (with Smart Drive) | $399 | Yes | Vivint Smart Drive ($249) |
| Vivint Doorbell Camera Pro | Doorbell | Yes (with Smart Drive) | $249 | Yes | Vivint Smart Drive ($249) |
| Nest Cam IQ Indoor | Indoor | Yes (with Nest Aware subscription) | $299 | Yes | None |
| Nest Cam Outdoor | Outdoor | Yes (with Nest Aware subscription) | $199 | Yes | None |
| Arlo Ultra 2 | Indoor/Outdoor | Yes (with Arlo Smart subscription) | $299 | Yes | Arlo SmartHub ($100) |
| EufyCam 2 Pro | Indoor/Outdoor | Yes (with Eufy Security subscription) | $150 | Yes | Eufy HomeBase 2 ($99) |
| Wyze Cam v3 | Indoor/Outdoor | Yes (with Cam Plus subscription) | $35 | Yes | None |
| Ring Stick Up Cam | Indoor/Outdoor | Yes (with Ring Alarm Pro + HD) | $100 | Yes | Ring Alarm Pro ($250), HD ($50) |
| Ring Indoor Cam | Indoor | Yes (with Ring Alarm Pro + HD) | $60 | Yes | Ring Alarm Pro ($250), HD ($50) |
| Ring Floodlight Cam Wired Pro | Outdoor | Yes (with Ring Alarm Pro + HD) | $250 | Yes | Ring Alarm Pro ($250), HD ($50) |
| Ring Spotlight Cam Wired | Outdoor | Yes (with Ring Alarm Pro + HD) | $200 | Yes | Ring Alarm Pro ($250), HD ($50) |
Notes:
- Vivint Smart Drive: The Smart Drive is essential for 24/7 recording and costs approximately $249. It stores up to 30 days of continuous footage.
- Subscriptions: Most systems require a subscription for cloud storage and advanced features:
- Vivint Subscription: Required for cloud storage and professional monitoring.
- Nest Aware: Starts at $6/month.
- Arlo Smart: Various plans starting at $2.99/month.
- Eufy Security: Starts at $2.99/month for single camera or $9.99/month for up to 10 cameras.
- Wyze Cam Plus: Starts at $1.25/month if billed annually.
- Ring Protect Plan: Necessary for 24/7 recording with local storage, starting at $3/month or $30/year.
Click Here To Get Vivent Free In Home Consultation
The evolution of surveillance cameras has been remarkable, from bulky and expensive closed-circuit television (CCTV) systems to sleek and affordable smart cameras like those offered by Ring. This evolution has been driven by advancements in technology, including improvements in video quality, motion detection algorithms, and wireless connectivity.
Concurrently, the popularity of smart home devices has surged in recent years, with more and more homeowners embracing connected technologies to enhance convenience, comfort, and security. Ring cameras exemplify this trend, seamlessly integrating with smart home ecosystems and providing users with unparalleled control and peace of mind over their living spaces.
History and development of Ring technology
Ring technology traces its origins back to 2013 when Jamie Siminoff, the founder and CEO, launched the company under the name Doorbot. The initial product was a smart doorbell equipped with a camera and motion sensors, allowing homeowners to see and communicate with visitors remotely via their smartphones. The idea stemmed from Siminoff’s desire to enhance home security and convenience, inspired by his own frustrations with missing deliveries and concerns about package theft.
The first generation of Doorbot faced challenges, including technical issues and limited market penetration. However, Siminoff’s vision remained steadfast, and he continued to refine the product and expand its capabilities. In 2014, the company rebranded as Ring, reflecting its broader mission to offer a range of innovative home security solutions beyond just doorbells.
Over the years, Ring technology has evolved significantly, incorporating advancements in hardware, software, and cloud computing. The introduction of Ring Video Doorbell Pro in 2016 marked a significant milestone, featuring enhanced video quality, customizable motion zones, and compatibility with existing doorbell wiring for easy installation. Subsequent iterations, such as the Ring Video Doorbell 2 and Ring Video Doorbell 3, further improved performance and added new features like rechargeable batteries and improved motion detection algorithms.
In addition to doorbells, Ring has expanded its product lineup to include indoor and outdoor security cameras, floodlights, and alarm systems, offering homeowners a comprehensive ecosystem of interconnected devices to protect their properties. The acquisition of other smart home companies, such as Mr. Beams and Zonoff, has further bolstered Ring’s portfolio and capabilities.
One of the key factors driving Ring’s success has been its focus on user experience and community engagement. The Neighbors app, launched in 2018, allows Ring users to share videos, report suspicious activities, and receive real-time crime and safety alerts from their local communities. This collaborative approach to home security has helped foster a sense of solidarity among users and contributed to Ring’s reputation as a leader in the smart home security industry.
Ring technology has undergone a remarkable journey of innovation and growth, from its humble beginnings as a smart doorbell startup to its current status as a global leader in home security solutions. With a commitment to quality, convenience, and community safety, Ring continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in the realm of smart home technology.
Functionality of Ring Cameras
Ring cameras offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance home security and provide users with peace of mind. From high-definition video recording to seamless integration with smart devices, these cameras are equipped with cutting-edge technology to meet the needs of modern homeowners.
Description of Ring camera features
- Video recording capabilities: Ring cameras capture crisp, clear video footage in high definition, allowing users to monitor their homes with clarity and detail. Whether it’s daytime or nighttime, these cameras deliver reliable performance, ensuring that users can always see what’s happening on their property.
- Two-way audio communication: One of the standout features of Ring cameras is their ability to facilitate two-way audio communication. This means that users can not only see but also speak to visitors or intruders through the camera’s built-in microphone and speaker. Whether it’s greeting a delivery person, scaring off a potential burglar, or simply checking in on pets, this feature adds an extra layer of interaction and security.
- Integration with mobile apps and smart devices: Ring cameras seamlessly integrate with the Ring mobile app, allowing users to access live video feeds, review recorded footage, and receive instant alerts from anywhere with an internet connection. Moreover, these cameras can be integrated with other smart devices and platforms, such as Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, enabling users to control their security system with voice commands and automate tasks for added convenience.
Explanation of motion detection technology
- How motion detection works in Ring cameras: Ring cameras utilize advanced motion detection technology to detect movement in their field of view. This technology relies on a combination of passive infrared (PIR) sensors and computer vision algorithms to distinguish between relevant motion, such as a person approaching the door, and irrelevant motion, such as a passing car or tree branch.
- Customization options for motion alerts: Users can customize motion detection settings to suit their preferences and specific needs. This includes adjusting sensitivity levels to reduce false alarms, defining motion zones to focus on specific areas of interest, and setting up custom schedules for when motion alerts are active. These customization options ensure that users receive timely and relevant alerts without being inundated with unnecessary notifications.
- Recording Capabilities: Ring cameras offer versatile recording capabilities, allowing users to capture and store footage of their surroundings for added security and peace of mind. Understanding these recording capabilities and storage options is essential for maximizing the utility of Ring cameras.
Discussion on continuous recording
- Clarification on 24/7 recording capabilities: While Ring cameras do not offer true 24/7 continuous recording like some traditional surveillance systems, they do provide a form of continuous monitoring through motion-activated recording. When motion is detected within the camera’s field of view, it triggers the camera to start recording, effectively capturing relevant events throughout the day and night.
- Factors influencing continuous recording: Several factors influence the effectiveness of continuous recording with Ring cameras. These include the camera’s placement and field of view, sensitivity settings for motion detection, and the presence of ambient light sources affecting the camera’s ability to capture clear footage in various lighting conditions.
Overview of storage options
Cloud storage vs. local storage
Ring cameras primarily offer cloud storage as the default option for storing recorded footage. Cloud storage provides the advantage of remote access to footage from anywhere with an internet connection, ensuring that users can review and download recordings even if the camera or local storage device is tampered with or stolen. However, cloud storage typically requires a subscription plan for access beyond a limited free trial period.
Alternatively, some Ring cameras also support local storage options, such as microSD cards or external hard drives connected to a base station. Local storage offers the benefit of not requiring ongoing subscription fees for access to recorded footage, but it may lack the convenience and accessibility of cloud storage for remote viewing and management.
Subscription plans and associated costs
Ring offers various subscription plans for cloud storage, with features such as extended video history, advanced motion detection settings, and professional monitoring services. The costs of these subscription plans vary depending on the number of cameras and desired features, ranging from affordable basic plans to more comprehensive premium plans. Users should carefully evaluate their recording and storage needs to choose the most suitable subscription plan for their requirements and budget
Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns surrounding Ring cameras encompass ethical considerations of constant surveillance and legal implications of recording activities. Understanding these concerns is crucial for both users and policymakers to navigate the complex landscape of home security and privacy rights.
Ethical considerations of constant surveillance
- Impact on personal privacy: Constant surveillance through Ring cameras raises questions about the erosion of personal privacy within the home. While the intention behind installing these cameras is often to enhance security, the continuous monitoring of private spaces can infringe upon individuals’ rights to privacy. Users must balance the benefits of surveillance with the need to respect the privacy of themselves, their families, and their visitors.
- Potential for misuse or abuse: The widespread adoption of Ring cameras also brings to light the potential for misuse or abuse of surveillance technology. Unauthorized access to camera feeds, hacking incidents, and data breaches pose significant risks to user privacy and security. Moreover, concerns have been raised about the potential for surveillance footage to be used for purposes beyond security, such as targeted advertising or law enforcement surveillance.
Legal implications of recording activities
- Regulations governing video surveillance: The use of Ring cameras is subject to various regulations and laws governing video surveillance, which vary by jurisdiction. These regulations typically address issues such as consent requirements for recording in public or semi-public spaces, restrictions on recording audio without consent, and guidelines for the retention and sharing of surveillance footage. Users must familiarize themselves with relevant laws and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid legal repercussions.
- Rights and responsibilities of homeowners: While homeowners have the right to use surveillance cameras to protect their property and ensure safety, they also have a responsibility to respect the privacy rights of others. This includes informing visitors and occupants of the presence of cameras, avoiding the placement of cameras in areas where privacy expectations are high (such as bedrooms or bathrooms), and securely storing and disposing of recorded footage to prevent unauthorized access.
Alternatives and Solutions
- Competing products and their features: Ring cameras are just one option among many in the market for home security camera systems. Competing products from companies like Nest, Arlo, and Wyze offer similar features such as motion detection, two-way audio, and cloud storage. Users should compare the features, pricing, and reputation of different camera systems to determine which best suits their needs.
- Pros and cons of different surveillance options: Each surveillance option comes with its own set of pros and cons. While Ring cameras offer convenience and integration with the Ring ecosystem, they may raise privacy concerns due to their association with Amazon and potential data sharing practices. Other options, such as self-hosted camera systems or open-source solutions, offer greater control over data and privacy but may require more technical expertise to set up and maintain.
Suggestions for privacy-conscious usage
- Tips for optimizing privacy settings: Users can take several steps to enhance privacy when using Ring cameras, such as regularly reviewing and adjusting privacy settings, disabling audio recording if not needed, and enabling two-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to camera feeds.
- Recommendations for responsible camera placement: Thoughtful placement of cameras can help balance security needs with privacy considerations. Users should avoid pointing cameras into neighboring properties, minimize coverage of private areas within their own property, and use privacy screens or adjustable privacy zones to mask sensitive areas from surveillance.
Conclusion
Ring cameras offer users a range of features, including high-definition video recording, two-way audio communication, and integration with mobile apps and smart devices. These capabilities make them a popular choice for home security and surveillance.
Potential users of Ring cameras should carefully consider the privacy implications of continuous surveillance and familiarize themselves with relevant laws and regulations governing video recording activities. By prioritizing privacy-conscious usage and responsible camera placement, users can mitigate privacy risks while still benefiting from the security and convenience offered by Ring cameras.
As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that home surveillance systems will become more advanced and sophisticated. Future developments may include improved privacy features, enhanced encryption protocols, and greater integration with artificial intelligence for smarter monitoring and detection capabilities. It is essential for users and policymakers to stay informed about these developments and actively engage in discussions surrounding privacy and security in the digital age.
Do Red Light Cameras Flash?
Red light cameras represent a critical component of modern traffic management systems, aimed at improving intersection safety and deterring red-light violations. This essay explores the definition and purpose of red light cameras, shedding light on their functionality and the significance of flash usage in capturing photographic evidence.
Red light cameras are automated traffic enforcement systems installed at intersections to detect and deter vehicles that run red lights. These cameras use sensors and imaging technology to monitor traffic signals and capture photographic evidence of vehicles violating traffic laws by entering intersections after the signal has turned red.
- Reducing Red-Light Running: Red light cameras discourage drivers from running red lights by capturing evidence of violations and issuing citations to offenders. This enforcement mechanism helps promote compliance with traffic signals and reduces the risk of collisions caused by red-light violations.
- Preventing Accidents: By deterring red-light running and enforcing traffic laws, red light cameras contribute to the prevention of intersection-related accidents, including side-impact collisions and pedestrian accidents. The presence of red light cameras serves as a visible reminder to motorists to obey traffic signals and exercise caution at intersections.
- Improving Law Enforcement: Red light cameras complement traditional law enforcement efforts by providing objective evidence of traffic violations. This enables law enforcement agencies to allocate resources more effectively, focusing on other enforcement priorities while leveraging technology to address red-light running and enhance public safety.
Functionality of Red Light Cameras
Red light cameras operate through a combination of detection mechanisms and image capture technology, enabling them to effectively monitor intersections and capture violations in real-time.
Detection Mechanism
- Vehicle Presence Detection: Red light cameras utilize sensors embedded in the roadway or mounted on traffic signal poles to detect the presence of vehicles approaching intersections. These sensors detect changes in magnetic fields or vehicle presence, triggering the camera system to activate when a vehicle enters the intersection during a red light phase.
- Signal Phasing Detection: Red light cameras are programmed to synchronize with traffic signal phasing, enabling them to distinguish between green, yellow, and red signal phases. By monitoring signal timing and phase changes, red light cameras accurately determine whether a vehicle has entered the intersection during a red light phase, indicating a potential violation.
Image Capture
- Continuous Monitoring: Red light cameras continuously monitor intersection activity, capturing video footage and still images of vehicles as they approach, enter, and exit the intersection. This continuous monitoring ensures comprehensive coverage of intersection activity and enables the camera system to capture violations effectively.
- Triggering Mechanism: When a red light violation is detected, the red light camera system is triggered to capture photographic evidence of the violation. This may involve capturing multiple images or video clips of the violating vehicle, including its license plate, position in the intersection, and relevant timestamps. The triggering mechanism ensures that only relevant violations are captured, minimizing false alarms and optimizing the use of camera resources.
Understanding Flash Usage in Red Light Cameras
Flash usage plays a crucial role in enhancing the visibility and accuracy of photographic evidence captured by red light cameras, particularly in low-light conditions or at nighttime.
Flash for Illumination
- Low Light Conditions: In low-light conditions, such as dawn, dusk, or inclement weather, visibility may be limited, affecting the quality of photographic evidence captured by red light cameras. Flash illumination helps overcome these visibility challenges by providing additional lighting to enhance image clarity and detail.
- Nighttime Operations: During nighttime operations, when ambient light levels are low, flash usage becomes essential for capturing clear images of vehicles and license plates. The bright flash helps illuminate the scene, ensuring that crucial details are captured accurately and facilitating the identification of violators.
Flash for Photographic Evidence
- Capturing License Plates: One of the primary functions of flash usage in red light cameras is to ensure the clear capture of license plate numbers. The bright flash helps eliminate shadows and glare, allowing the camera system to capture sharp, legible images of license plates, even at high speeds or in adverse lighting conditions.
- Identifying Drivers: In addition to capturing license plate numbers, flash illumination aids in identifying drivers and occupants of vehicles involved in red-light violations. By illuminating the interior of the vehicle, the flash helps capture images of the driver’s face or other identifying features, facilitating law enforcement efforts and citation processing.
Red light cameras play a crucial role in promoting intersection safety and enforcing traffic laws by deterring red-light violations and capturing photographic evidence of offenders. Understanding the functionality and importance of flash usage in red light cameras is essential for optimizing their effectiveness in enhancing traffic safety and compliance. By leveraging advanced technology and enforcement mechanisms, red light cameras contribute to the creation of safer and more efficient transportation networks, ultimately saving lives and reducing accidents at intersections.
Factors Influencing Flash Activation
Red light cameras utilize flash activation to ensure the clarity and accuracy of photographic evidence captured during red-light violations. Several factors influence the activation of the flash, including environmental conditions, camera configuration, and legal requirements.
Environmental Conditions
- Ambient Light Levels: Ambient light levels play a significant role in determining the necessity of flash activation. In well-lit environments during the daytime, where natural or artificial lighting is sufficient, the flash may not be activated. However, in low-light conditions such as early morning, evening, or overcast weather, the flash becomes essential to illuminate the scene and capture clear images.
- Weather Conditions: Weather conditions such as rain, fog, or snow can further reduce visibility and necessitate flash activation. Adverse weather conditions may obscure the view of the intersection or create glare, making it challenging to capture photographic evidence without adequate illumination from the flash.
Camera Configuration
- Sensitivity Settings: Red light cameras are equipped with sensitivity settings that determine when the flash is activated based on the detected ambient light levels and traffic conditions. Adjustments to sensitivity settings enable the camera system to adapt to changing lighting conditions and ensure consistent performance in various environments.
- Flash Intensity Control: The intensity of the flash can be adjusted to suit the specific requirements of the intersection and prevailing lighting conditions. Higher flash intensity may be required in low-light situations to compensate for reduced visibility, while lower intensity settings may suffice in well-lit environments to avoid excessive glare or discomfort to drivers.
Legal Requirements
- Jurisdictional Regulations: The activation of the flash in red light cameras is governed by jurisdictional regulations and laws pertaining to traffic enforcement and surveillance. Legal requirements may dictate the circumstances under which the flash can be activated, such as specific thresholds for ambient light levels or weather conditions, to ensure compliance with privacy and safety standards.
- Operational Guidelines: Law enforcement agencies and traffic authorities may establish operational guidelines for the use of red light cameras and flash activation. These guidelines may include protocols for determining when to activate the flash, procedures for reviewing captured footage, and standards for maintaining the integrity of photographic evidence in accordance with legal requirements.
Alternatives to Flash Usage
While flash activation is commonly used in red light cameras to enhance visibility and capture photographic evidence, alternative illumination methods exist to achieve similar objectives.
Infrared Illumination
- Invisible to Human Eye: Infrared (IR) illumination offers an alternative to visible flash activation, emitting light in the infrared spectrum that is invisible to the human eye. This allows red light cameras to illuminate the scene discreetly without alerting drivers to the presence of the camera or causing distraction.
- Enhanced Night Vision: IR illumination enhances night vision capabilities, enabling red light cameras to capture clear images in low-light or nighttime conditions. By leveraging IR technology, red light cameras can overcome visibility challenges and maintain surveillance effectiveness without relying on visible flash activation.
Ambient Light Utilization
- Natural Lighting Conditions: Red light cameras can utilize natural lighting conditions, such as sunlight or streetlights, to illuminate the scene and capture photographic evidence without the need for artificial flash activation. By leveraging available ambient light, red light cameras can minimize disruption to drivers and pedestrians while ensuring accurate enforcement of traffic laws.
- Artificial Lighting Sources: In well-lit environments or urban areas with ample artificial lighting, red light cameras may rely on existing light sources, such as streetlights or traffic signals, to illuminate the intersection and capture clear images. By optimizing ambient light utilization, red light cameras can reduce energy consumption and mitigate potential concerns associated with visible flash activation.
Public Perception and Concerns
The use of flash activation in red light cameras can influence public perception and give rise to various concerns related to driver behavior, privacy, and intrusion.
Effect on Driver Behavior
- Awareness of Flash: The activation of the flash in red light cameras may alert drivers to the presence of the camera and influence their behavior at intersections. Drivers who are aware of the flash may be more cautious and compliant with traffic signals, reducing the likelihood of red-light violations and improving overall intersection safety.
- Potential Distraction: Visible flash activation may also serve as a distraction to drivers, particularly in low-light conditions or adverse weather. The sudden burst of light may momentarily divert drivers’ attention from the road ahead, posing a safety risk and potentially contributing to accidents or near misses.
Privacy Considerations
- Intrusiveness of Flash: The visible flash from red light cameras may be perceived as intrusive or invasive by some individuals, raising concerns about privacy and surveillance. The conspicuous nature of the flash may evoke feelings of discomfort or unease among drivers and pedestrians, particularly if they are unaware of the purpose of the camera or its operational status.
- Capture of Surrounding Activity: Flash activation in red light cameras has the potential to capture surrounding activity beyond the intended target, including vehicles, pedestrians, and nearby residences. This broad scope of surveillance may encroach upon individuals’ privacy rights and give rise to concerns about the indiscriminate collection of personal data and the erosion of civil liberties.
Conclusion
The activation of flash in red light cameras serves a crucial role in enhancing intersection safety, enforcing traffic laws, and capturing photographic evidence of violations. By considering factors such as environmental conditions, camera configuration, and legal requirements, traffic authorities can optimize flash activation to ensure effective surveillance while minimizing disruption to drivers and pedestrians
Red light cameras utilize flash activation to enhance visibility and capture clear images of red-light violations, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of photographic evidence for law enforcement purposes.
The effective use of flash activation in red light cameras contributes to improved traffic safety, reduced red-light violations, and enhanced compliance with traffic laws, ultimately leading to safer roadways and fewer accidents at intersections.
As technology continues to evolve, red light camera systems may incorporate advanced features such as infrared illumination, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data analytics to enhance surveillance capabilities and address emerging challenges in traffic enforcement and safety.
Flash activation in red light cameras plays a vital role in promoting intersection safety, enforcing traffic laws, and protecting public safety. By understanding the factors influencing flash activation and considering alternative illumination methods, traffic authorities can optimize the effectiveness of red light camera systems while addressing public concerns and privacy considerations.
Choosing the Right Home Security Camera: A Comprehensive Guide
In an era marked by technological advancements and evolving safety concerns, the significance of home security cameras in modern security systems cannot be overstated. As crime rates fluctuate and safety becomes an increasing priority for homeowners, the demand for home security cameras continues to soar. This essay aims to explore the importance of home security cameras, the driving forces behind their growing demand, and the purpose of providing a comprehensive guide for selecting the right camera for individual needs.
Home security cameras serve as a critical component of modern security setups, offering homeowners unparalleled peace of mind and protection. With the ability to monitor activities both inside and outside the home, these cameras act as vigilant guardians, deterring potential intruders and capturing crucial evidence in the event of a security breach. By providing real-time surveillance footage and remote access capabilities, they empower homeowners to keep a watchful eye on their property even when they’re away, ensuring the safety of their loved ones and belongings.
The purpose of this essay is to serve as a comprehensive guide for individuals navigating the vast landscape of home security cameras. By outlining key considerations, comparing different camera types, and offering insights into essential features and functionalities, this guide aims to empower readers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions when choosing a home security camera. Whether it’s ensuring high-definition resolution for clear footage, evaluating night vision capabilities, or selecting the appropriate power source and connectivity options, this guide will cover all aspects essential to selecting the right camera to meet specific surveillance needs and preferences.
Home Security Camera Types
Home security cameras come in various types designed to cater to diverse surveillance requirements and environments. These include indoor cameras, outdoor cameras, wired cameras, and wireless cameras. Each type offers distinct advantages and functionalities suited to specific usage scenarios, making it essential for homeowners to understand their options before making a purchase decision.
Comparison of Features and Functionalities Offered by Various Camera Types
When comparing different camera types, it’s crucial to consider factors such as resolution, field of view, night vision capabilities, and connectivity options. Indoor cameras, for instance, are typically compact and discreet, ideal for monitoring interior spaces such as living rooms, nurseries, or home offices. Outdoor cameras, on the other hand, are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and offer features like weatherproofing and infrared night vision for reliable outdoor surveillance.
Considerations for Specific Surveillance Needs and Preferences
Understanding the basic distinctions between camera types, homeowners should also consider their specific surveillance needs and preferences. Factors such as the size of the property, the presence of potential blind spots, and the desired level of monitoring granularity will influence the choice of camera type and features. For example, larger properties may require multiple cameras with wide-angle lenses to ensure comprehensive coverage, while homeowners with privacy concerns may opt for cameras with advanced encryption features for enhanced data security.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Home Security Camera
Resolution and Image Quality: Importance of High-Definition Resolution for Clear Footage
One of the primary factors to consider when choosing a home security camera is resolution and image quality. High-definition (HD) resolution ensures crisp, clear footage that is essential for identifying intruders or capturing important details such as license plate numbers or facial features. Cameras with higher resolution capabilities, such as 1080p or 4K, offer superior image clarity and are ideal for situations where precise identification is paramount.
Field of View: Evaluating the Camera’s Coverage Area and Viewing Angle
The field of view (FOV) refers to the extent of the area that a camera can capture, typically measured in degrees. Cameras with wider FOVs can monitor larger areas with fewer blind spots, making them suitable for open spaces such as yards or driveways. Conversely, cameras with narrower FOVs may be more appropriate for focused surveillance of specific entry points or corridors. Additionally, the viewing angle of the camera lens influences the FOV, with wide-angle lenses providing expansive coverage and fisheye lenses offering panoramic views.
Night Vision Capabilities: Ensuring Visibility in Low-Light or Nighttime Conditions
Effective night vision capabilities are essential for maintaining surveillance visibility in low-light or nighttime conditions. Infrared (IR) LEDs illuminate the camera’s field of view, allowing it to capture clear footage even in complete darkness. Cameras with advanced night vision technology offer extended range and clarity, enabling homeowners to monitor their property around the clock without compromising on image quality.
Power Source: Choosing Between Wired, Battery-Powered, or Solar-Powered Cameras
Home security cameras can be powered by various sources, including wired connections, batteries, or solar panels. Wired cameras offer continuous power supply and are ideal for permanent installations where reliability is paramount. Battery-powered cameras, on the other hand, offer flexibility and easy setup, making them suitable for temporary or remote surveillance applications. Solar-powered cameras harness solar energy to recharge their batteries, providing a sustainable and eco-friendly power solution for outdoor installations.
Connectivity Options: Considering Wi-Fi, Cellular, or Ethernet Connectivity for Remote Access
The connectivity options available for home security cameras play a crucial role in enabling remote access and monitoring. Wi-Fi connectivity allows cameras to connect to a home network, facilitating seamless integration with smartphones, tablets, or computers for real-time viewing and control.
Cellular connectivity provides an alternative connection method, allowing cameras to transmit footage over cellular networks in areas with limited or unreliable Wi-Fi coverage. Ethernet connectivity offers a wired connection option for enhanced stability and security, particularly in scenarios where wireless interference or hacking risks are a concern.
Storage Options: Exploring Local Storage, Cloud Storage, or Both for Footage Storage
Finally, homeowners must consider the storage options available for storing surveillance footage captured by home security cameras. Local storage solutions, such as onboard SD card slots or network-attached storage (NAS) devices, offer convenience and control over data management but may be susceptible to theft or damage.
Cloud storage services provide offsite backup and accessibility, allowing footage to be securely stored and accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. Some cameras offer hybrid storage solutions, allowing footage to be stored locally and backed up to the cloud for added redundancy and peace of mind.
Home security cameras offer a range of features and considerations that are vital for ensuring effective surveillance and peace of mind. Understanding these key aspects can help homeowners make informed decisions when selecting the right camera for their needs.
- Motion Detection: Motion detection is a fundamental feature of home security cameras, enabling them to detect and record any movement within their field of view. By triggering alerts and recording footage when motion is detected, these cameras can effectively capture suspicious activity and provide timely notifications to homeowners. Understanding how motion detection works and its sensitivity settings is crucial for minimizing false alarms while ensuring reliable detection of potential threats.
- Two-Way Audio: Two-way audio capability allows homeowners to communicate through the camera’s built-in microphone and speaker. This feature facilitates real-time interaction with visitors, delivery personnel, or family members, enhancing security and convenience. Whether it’s deterring intruders with a warning message or remotely communicating with loved ones, two-way audio adds an extra layer of functionality to home security cameras.
- Smart Home Integration: Integration with smart home platforms and voice assistants enables seamless control and automation of home security systems. Compatible cameras can be integrated with popular platforms such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit, allowing users to monitor and control their cameras using voice commands or through centralized smart home apps. This interoperability enhances convenience and expands the capabilities of home security systems by integrating them into broader smart home ecosystems.
- Weather Resistance: For outdoor surveillance applications, weather resistance is essential to ensure durability and reliability in challenging environmental conditions. Weatherproof cameras are designed to withstand exposure to elements such as rain, snow, and extreme temperatures, ensuring continuous operation and longevity. By investing in weather-resistant cameras, homeowners can safeguard their property against outdoor threats without compromising on performance or reliability.
- Privacy Features: Privacy-enhancing features such as encryption and privacy zones are crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining privacy. Encryption ensures that surveillance footage is securely transmitted and stored, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or interception. Privacy zones allow users to designate specific areas within the camera’s field of view where recording is prohibited, such as windows or neighboring properties, preserving privacy while still capturing essential footage.
Budget and Cost Considerations
When purchasing home security cameras, it’s essential to consider budget and total cost of ownership to find the best value option without compromising on essential features and functionality.
- Setting a Budget: Setting a budget for home security camera purchase and installation helps homeowners narrow down their options and prioritize essential features within their price range. By establishing a budget upfront, homeowners can avoid overspending and ensure that their investment aligns with their financial constraints.
- Evaluating Total Cost of Ownership: In addition to the initial purchase cost, homeowners should consider additional expenses such as installation fees, accessories, and subscription fees for cloud storage or advanced features. Assessing the total cost of ownership helps ensure that the chosen camera system remains affordable and sustainable over the long term.
- Balancing Cost with Desired Features: Finding the right balance between cost and desired features is key to maximizing value and satisfaction with a home security camera system. While budget-friendly options may offer basic functionality, higher-priced models may provide advanced features and capabilities that justify the additional investment. By weighing the cost against desired features and performance, homeowners can make informed decisions that meet their security needs without breaking the bank.
Researching and Comparing Camera Brands and Models
Before making a purchase decision, homeowners should conduct thorough research and comparison of camera brands and models to ensure quality, reliability, and compatibility with their needs.
- Researching Reputable Brands: Researching reputable camera brands known for quality and reliability helps homeowners narrow down their options and identify trusted manufacturers with a proven track record. Established brands with a history of innovation and customer satisfaction are more likely to deliver superior performance and support, making them preferred choices for home security solutions.
- Reading Customer Reviews: Reading customer reviews and feedback provides valuable insights into user satisfaction, reliability, and performance of different camera models. Real-world experiences shared by other homeowners can help prospective buyers gauge the pros and cons of specific cameras and make informed decisions based on peer recommendations and experiences.
- Comparing Specifications and Features: Comparing specifications, features, and prices of different camera models allows homeowners to evaluate their options comprehensively and identify the best fit for their needs. Key factors to consider include resolution, field of view, night vision capabilities, connectivity options, and smart home integration. By comparing cameras side by side, homeowners can identify the most suitable option that meets their requirements and preferences.
Installation and Setup Process
Once a home security camera system has been selected, homeowners must consider the installation and setup process to ensure proper functionality and performance.
- Assessing Installation Requirements: Assessing installation requirements and compatibility with existing home infrastructure helps homeowners plan and prepare for the installation process. Factors to consider include mounting options, power source availability, and network connectivity, as well as any additional equipment or accessories needed for installation.
- Understanding Setup Process: Understanding the setup process and any technical considerations involved ensures smooth installation and setup of home security cameras. This may involve configuring camera settings, connecting to a Wi-Fi network, and installing accompanying mobile apps or software for remote access and control. Following manufacturer instructions and guidelines is essential to ensure proper setup and optimal performance of the camera system.
- Tips for Proper Installation: Proper installation and positioning of home security cameras are critical for maximizing coverage and effectiveness. Cameras should be strategically placed to cover entry points, vulnerable areas, and high-traffic areas while minimizing blind spots and obstructions. Additionally, ensuring secure mounting and weatherproofing outdoor cameras can prolong their lifespan and maintain reliable operation in outdoor environments.
Warranty and Support Options
Reviewing warranty coverage and support options provided by camera manufacturers is essential for ensuring ongoing reliability and peace of mind.
- Reviewing Warranty Coverage: Reviewing warranty coverage helps homeowners understand their rights and entitlements in case of product defects or malfunctions. Warranty duration, coverage limits, and exclusions vary between manufacturers, so it’s essential to carefully review warranty terms and conditions to assess the level of protection provided.
- Understanding Support Options: Understanding the process for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues is crucial for accessing timely support and assistance when needed. Manufacturers may offer various support channels, including phone support, email support, live chat, or online knowledge bases. Familiarizing oneself with available support options and resources can expedite issue resolution and minimize downtime for home security cameras.
- Considering Extended Warranty or Support Plans: Considering extended warranty or support plans can provide added peace of mind and protection beyond the standard warranty period. Extended warranty plans typically offer extended coverage and additional benefits such as priority support, onsite repairs, or replacement of defective units. While optional, these plans can offer valuable protection and support for homeowners seeking enhanced coverage and support for their investment.
Conclusion
Selecting the right home security camera involves careful consideration of key features, budget and cost considerations, brand and model research, installation and setup process, and warranty and support options.
By understanding these factors and following the comprehensive guide outlined in this essay, homeowners can make informed decisions and invest in a reliable home security solution that enhances safety and peace of mind for themselves and their loved ones.
Encouraging readers to leverage the insights and recommendations provided in this guide, I emphasize the importance of selecting the right home security camera system to safeguard their property and enjoy enhanced security and convenience in their daily lives.
Can a TV Screen Be Used As a Camera?
In the modern age of technology, the convergence of devices and functionalities continues to redefine the boundaries of innovation. Among these advancements is the concept of utilizing TV screens not only for displaying images but also as cameras. In this introduction, we will explore the definition of TV screens and introduce the intriguing concept of repurposing them as cameras.
A TV screen, short for television screen, is the display component of a television set. It consists of a flat or curved panel that emits light to produce visual images, allowing viewers to watch television programs, movies, and other multimedia content. TV screens come in various sizes, resolutions, and technologies, including LCD (liquid crystal display), LED (light-emitting diode), OLED (organic light-emitting diode), and QLED (quantum dot LED).
Traditionally, TV screens have been passive receivers of visual information, relying on external sources such as broadcast signals, streaming devices, or connected peripherals to display content. However, recent technological advancements have enabled TV screens to take on a more active role by integrating camera functionality directly into their design. This innovative approach transforms TV screens into multifunctional devices capable of capturing, processing, and displaying visual imagery without the need for separate camera equipment.
Technical Feasibility
The technical feasibility of using a TV screen as a camera hinges on understanding the underlying principles of both display technology and camera functionality.
Explanation of How a TV Screen Works
TV screens operate by illuminating individual pixels to create images. In LCD and LED TVs, liquid crystals or LEDs behind the screen selectively block or allow light to pass through, forming images composed of millions of tiny pixels. OLED and QLED TVs utilize organic compounds or quantum dots to emit light directly, resulting in vibrant colors and high contrast ratios. By manipulating the intensity and color of light emitted by each pixel, TV screens can render lifelike images with impressive clarity and detail.
Discussion on the Components Required for Camera Functionality
To repurpose a TV screen as a camera, several essential components are required, including imaging sensors, lenses, image processors, and software algorithms. Imaging sensors, such as CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) or CCD (charge-coupled device) chips, capture incoming light and convert it into electrical signals representing image data. Lenses focus light onto the sensor, while image processors analyze and enhance the captured images. Software algorithms play a crucial role in image processing, enabling features such as autofocus, exposure control, and image stabilization.
Examination of Potential Technical Challenges and Limitations
Despite its innovative potential, repurposing a TV screen as a camera poses several technical challenges and limitations. One primary concern is the limited space available within the slim form factor of modern TV screens, which may constrain the size and performance of integrated camera components.
Additionally, achieving high-quality image capture and processing capabilities comparable to dedicated cameras may require significant advancements in sensor technology, optics, and computational imaging algorithms. Furthermore, ensuring compatibility with existing TV hardware and software ecosystems presents additional hurdles that must be addressed to realize the full potential of this concept.
Current Applications and Research
While the concept of using TV screens as cameras is still in its infancy, there have been notable developments and research efforts aimed at exploring its feasibility and potential applications.
Several research studies and experimental projects have investigated the possibility of repurposing TV screens as cameras. These efforts often focus on leveraging existing TV hardware and software infrastructure to integrate camera functionality seamlessly. Research teams have explored various approaches, including utilizing the backlighting system of LED TVs as a light source for imaging, embedding miniature cameras behind OLED display panels, and developing software algorithms for image processing and analysis.
Discussion on Practical Applications or Prototypes Developed
Practical applications of using TV screens as cameras span a wide range of domains, including augmented reality (AR), video conferencing, surveillance, and interactive displays. Prototypes and proof-of-concept demonstrations have showcased the potential of this technology in enabling immersive AR experiences, facilitating remote communication through virtual meetings, enhancing home security with integrated surveillance capabilities, and creating interactive digital signage solutions.
These developments underscore the versatility and adaptability of TV screens as camera-enabled devices capable of enriching various aspects of daily life.
Examination of Advantages and Disadvantages in Specific Contexts
The adoption of TV screens as cameras offers several advantages, including space-saving integration, simplified setup and installation, and seamless user experience. By consolidating multiple functionalities into a single device, TV screens equipped with cameras can streamline workflows, reduce clutter, and enhance user convenience.
However, potential disadvantages such as compromises in image quality, limited flexibility in camera positioning, and concerns regarding privacy and security must be carefully considered and addressed to ensure widespread acceptance and adoption of this technology.
The concept of using TV screens as cameras represents a promising frontier in the evolution of display technology and imaging systems. While technical challenges and limitations remain, ongoing research and development efforts continue to push the boundaries of innovation, paving the way for new applications and experiences that leverage the convergence of display and imaging capabilities. As this technology matures, we can expect to see increasingly sophisticated implementations and novel use cases that transform how we interact with and perceive the world around us.
Technology and Innovation
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the capabilities of TV screens, enabling them to take on new roles beyond traditional display functions. In this section, we’ll explore the emerging technologies that facilitate the integration of camera functionality into TV screens, as well as the advancements in sensor technology, image processing, and display capabilities that drive innovation in this field.
Exploration of Emerging Technologies Enabling TV Screens to Function as Cameras
Emerging technologies play a pivotal role in enabling TV screens to function as cameras. One such technology is transparent OLED (organic light-emitting diode) displays, which combine the properties of OLED technology with transparent substrates to create see-through displays capable of capturing images through the screen itself.
This breakthrough allows TV screens to seamlessly transition between display and camera modes, opening up new possibilities for interactive applications and augmented reality experiences.
Another enabling technology is AI-driven image processing algorithms, which leverage machine learning and computer vision techniques to enhance the capabilities of TV screen cameras. These algorithms enable features such as facial recognition, gesture detection, and object tracking, transforming TV screens into intelligent imaging devices capable of understanding and responding to their surroundings.
Discussion on Advancements in Sensor Technology, Image Processing, and Display Capabilities
Advancements in sensor technology have played a crucial role in enhancing the performance and functionality of TV screen cameras. Miniaturized CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) and CCD (charge-coupled device) sensors enable high-resolution imaging with improved sensitivity and dynamic range, while advances in lens design and optics contribute to sharper focus and reduced distortion.
Furthermore, rapid developments in image processing algorithms have revolutionized the capabilities of TV screen cameras. Real-time image enhancement techniques such as noise reduction, dynamic range optimization, and color correction improve image quality under challenging lighting conditions, while advanced autofocus and exposure control algorithms ensure sharp, well-exposed images in any environment.
In terms of display capabilities, TV screens continue to evolve with advancements in resolution, refresh rate, and color accuracy. High-resolution displays such as 4K and 8K panels deliver unparalleled image clarity and detail, while high refresh rates and HDR (high dynamic range) support provide smooth motion and lifelike colors. These advancements not only enhance the viewing experience but also contribute to the quality and fidelity of images captured by TV screen cameras.
Analysis of Potential Future Developments and Their Implications
Looking ahead, the future of TV screen cameras holds immense potential for innovation and disruption across various industries. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further integration of AI-driven features, such as scene recognition, image segmentation, and content-based image retrieval, which will enhance the intelligence and versatility of TV screen cameras.
Additionally, advancements in 3D imaging and depth sensing technologies may enable TV screens to capture spatial information and create immersive holographic displays, blurring the line between physical and virtual reality. Furthermore, the integration of biometric sensors and health monitoring capabilities into TV screen cameras could revolutionize the way we interact with and use these devices, opening up new opportunities for personalized entertainment, wellness tracking, and telemedicine.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations
While the integration of camera functionality into TV screens offers numerous benefits, it also raises important ethical and privacy concerns that must be carefully addressed.
- Discussion on Ethical Implications of Using TV Screens as Cameras, Including Surveillance Concerns: The use of TV screens as cameras raises concerns about potential surveillance and privacy violations. With the ability to capture images and video footage of individuals in their homes, there is a risk of unauthorized surveillance and intrusion into personal privacy. Furthermore, the integration of AI-driven features such as facial recognition and behavioral analysis raises concerns about the potential misuse of sensitive data and the infringement of individual rights.
- Examination of Privacy Considerations Related to Potential Data Collection and Usage: Privacy considerations related to data collection and usage are another significant concern associated with TV screen cameras. Manufacturers and service providers may collect and store user data for various purposes, including advertising, analytics, and product improvement. However, the collection and processing of personal data raise concerns about data security, consent, and transparency, as well as the potential for misuse or unauthorized access.
- Exploration of Regulatory Frameworks and Guidelines Addressing These Concerns: To address these ethical and privacy concerns, regulatory frameworks and guidelines governing the use of TV screen cameras are essential. Governments and regulatory bodies may establish rules and standards regarding data privacy, surveillance practices, and consumer rights to ensure the responsible and ethical use of TV screen cameras. Additionally, industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, developers, and service providers, have a responsibility to implement robust privacy policies, security measures, and transparency mechanisms to safeguard user privacy and mitigate potential risks.
Practical Considerations and Challenges
Despite the promising potential of TV screen cameras, several practical considerations and challenges must be addressed to realize their full benefits.
- Discussion on Practical Considerations Such as Cost, Scalability, and Usability: Cost, scalability, and usability are significant practical considerations when deploying TV screen cameras. The integration of camera functionality into TV screens may add to the cost of manufacturing and development, potentially impacting the affordability and accessibility of these devices. Additionally, ensuring scalability and compatibility across different TV models and manufacturers presents challenges related to standardization and interoperability. Furthermore, usability considerations such as user interface design, accessibility features, and ease of installation are essential for ensuring a seamless and intuitive user experience.
- Examination of Challenges Related to Image Quality, Resolution, and Field of View: Challenges related to image quality, resolution, and field of view are critical factors influencing the performance and effectiveness of TV screen cameras. Maintaining high image quality and resolution while minimizing distortion and aberrations requires careful design and optimization of camera optics, sensors, and processing algorithms. Furthermore, ensuring adequate coverage and visibility across a wide field of view presents challenges in terms of lens design, sensor placement, and image processing techniques.
- Analysis of Potential Solutions and Strategies to Overcome These Challenges: To overcome these challenges, manufacturers and developers may employ various strategies and solutions. Investing in research and development to advance sensor technology, optics, and image processing algorithms can improve image quality and resolution while reducing costs and scalability issues.
Additionally, implementing user-friendly interfaces, automated calibration procedures, and remote troubleshooting capabilities can enhance the usability and accessibility of TV screen cameras. Furthermore, collaborating with industry partners, regulatory bodies, and stakeholders to establish standards and best practices can ensure consistency, interoperability, and compliance with ethical and privacy principles.
Conclusion
The integration of camera functionality into TV screens represents a transformative development with vast implications for technology, innovation, and society. By leveraging emerging technologies, such as transparent displays, AI-driven image processing, and biometric sensors, TV screens have the potential to become versatile imaging devices capable of enhancing entertainment, communication, and productivity in diverse applications.
However, ethical and privacy considerations must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible and ethical use of TV screen cameras, while practical challenges related to cost, scalability, and usability require innovative solutions and collaborative efforts. As technology continues to evolve, the future of TV screen cameras holds promise for creating immersive experiences, empowering users, and shaping the way we interact with digital media and information.
Best Batteries for Trail Cameras
Trail cameras have revolutionized wildlife monitoring and outdoor photography, providing enthusiasts and professionals alike with a unique window into the natural world. However, the reliability and performance of these cameras are contingent upon the batteries that power them. This introduction provides an overview of trail camera batteries, underscores the importance of selecting the best batteries, and outlines the purpose of the topic, which is to explore various battery options and considerations for optimal trail camera performance.
Trail cameras rely on batteries to capture images and videos of wildlife in remote locations. These cameras are designed to operate for extended periods in outdoor environments where access to power sources is limited or nonexistent. As such, selecting the right batteries is crucial to ensure uninterrupted operation and reliable performance.
Choosing the appropriate batteries for trail cameras is paramount for several reasons. Firstly, batteries directly impact camera performance, including image capture speed, trigger time, and overall reliability. Secondly, selecting high-quality batteries can extend the lifespan of the camera and minimize the frequency of battery replacements, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Moreover, the right batteries can enhance the camera’s performance in extreme weather conditions, ensuring continued operation in harsh environments.
The purpose of this topic outline is to delve into the intricacies of trail camera batteries, including different types, factors to consider when choosing batteries, and comparisons of top battery brands and models. By providing comprehensive guidance on battery selection, this guide aims to empower trail camera users to make informed decisions that optimize camera performance and longevity.
Trail Camera Battery Types
Trail cameras are compatible with various battery types, each offering unique advantages and considerations.
- Alkaline Batteries: Pros and Cons: Alkaline batteries are widely available and affordable, making them a popular choice for trail cameras. However, they have limited lifespan and performance, particularly in cold temperatures, making them less suitable for long-term use in outdoor environments.
- Lithium Batteries: Advantages and Limitations: Lithium batteries, such as Energizer Ultimate Lithium, offer superior performance and longevity compared to alkaline batteries. They provide reliable power output in extreme temperatures and have a longer shelf life, making them ideal for extended use in outdoor settings. However, lithium batteries are more expensive upfront, which may deter some users.
- Rechargeable Batteries: Benefits and Considerations: Rechargeable batteries, such as Eneloop and Tenergy Rechargeable, offer cost savings and environmental benefits compared to disposable batteries. They can be recharged hundreds of times, reducing waste and long-term expenses. However, rechargeable batteries may have lower voltage output compared to disposable options, affecting camera performance, and require access to power sources for recharging.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Batteries
Several factors should be taken into account when selecting batteries for trail cameras to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
- Battery Life: Longevity and Performance Under Varying Conditions: Battery life is a critical consideration, especially for users who require extended camera operation without frequent battery replacements. Assessing battery life under different conditions, such as temperature extremes and usage frequency, helps determine the most suitable battery type for specific needs.
- Weather Resistance: Ability to Withstand Extreme Temperatures and Weather Conditions: Trail cameras are often deployed in outdoor environments where they are exposed to harsh weather conditions, including extreme temperatures, rain, and humidity. Choosing batteries with excellent weather resistance ensures reliable performance and minimizes the risk of camera failure due to adverse weather.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Balance Between Upfront Cost and Long-Term Value: While disposable batteries may have lower upfront costs, rechargeable batteries offer long-term cost savings due to their reusability. Considering the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase price and ongoing expenses, helps determine the most cost-effective battery option over the camera’s lifespan.
- Compatibility: Ensuring Compatibility With Specific Trail Camera Models: Not all batteries are compatible with every trail camera model. It is essential to verify compatibility with the camera manufacturer’s recommendations to avoid potential compatibility issues and ensure optimal performance.
- Environmental Impact: Considerations for Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness: Choosing environmentally friendly battery options, such as rechargeable batteries, contributes to sustainability efforts and reduces the environmental impact of battery disposal. Considering the ecological footprint of batteries helps align with conservation values and minimize environmental harm.
Comparison of Top Battery Brands And Models
Several battery brands and models are available on the market, each offering distinct features and performance characteristics.
- Review of Popular Alkaline Battery Brands (e.g., Duracell, Energizer): Alkaline batteries from reputable brands like Duracell and Energizer are widely used for their affordability and availability. These batteries provide adequate power output for trail cameras but may have shorter lifespan and performance compared to lithium options.
- Examination of Leading Lithium Battery Options (e.g., Energizer Ultimate Lithium, Tenergy): Lithium batteries, such as Energizer Ultimate Lithium and Tenergy, offer superior performance and longevity compared to alkaline batteries. They are ideal for outdoor use, providing reliable power output in extreme temperatures and harsh conditions.
- Evaluation of Rechargeable Battery Brands and Models (e.g., Eneloop, Tenergy Rechargeable): Rechargeable batteries, such as Eneloop and Tenergy Rechargeable, offer cost savings and environmental benefits compared to disposable options. These batteries can be recharged hundreds of times, making them suitable for frequent camera use and reducing waste.
Selecting the best batteries for trail cameras is essential for ensuring reliable performance and longevity in outdoor environments. By understanding different battery types, considering factors such as battery life and weather resistance, and comparing top battery brands and models, trail camera users can make informed decisions that optimize camera performance and minimize maintenance costs. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into battery selection, empowering users to maximize the effectiveness and longevity of their trail camera systems.
Performance Testing and Reviews
To ensure optimal performance of trail cameras, thorough testing and reviews of battery options are essential. This section explores independent battery performance tests, user experiences, and real-world comparisons to aid in selecting the most suitable batteries for trail cameras.
- Independent Battery Performance Tests Conducted by Experts: Expert-led independent tests provide valuable insights into battery performance, including factors such as longevity, reliability, and suitability for outdoor use. These tests assess various battery types under controlled conditions, helping users make informed decisions based on objective data.
- Analysis of User Reviews and Experiences with Different Battery Brands and Models: User reviews offer firsthand accounts of battery performance in real-world scenarios, providing valuable feedback on factors such as durability, reliability, and longevity. Analyzing user experiences helps identify trends and patterns across different battery brands and models, aiding in decision-making.
- Comparison of Battery Performance in Real-World Trail Camera Settings: Comparing battery performance in real-world trail camera settings offers practical insights into how different batteries fare in outdoor environments. Factors such as weather resistance, temperature tolerance, and longevity under continuous use are evaluated to assess overall performance.
Tips for Maximizing Battery Life
Maximizing battery life is essential for prolonged trail camera operation and reduced maintenance. This section provides practical tips and strategies for optimizing battery performance and longevity.
- Proper Battery Installation and Maintenance Tips: Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for maximizing battery life. Ensure batteries are inserted correctly, and contacts are clean to minimize power loss. Regularly inspect and clean battery compartments to prevent corrosion and ensure optimal contact.
- Strategies for Conserving Battery Power in Trail Cameras: Conserving battery power is essential for extending camera operation between replacements. Adjusting camera settings such as trigger interval, resolution, and flash usage can significantly impact battery life. Opt for lower settings when extended surveillance periods are not required to conserve power.
- Recommendations for Extending Battery Life in Different Weather Conditions: Extreme temperatures can affect battery performance. In hot climates, provide shade for cameras to prevent overheating, while insulating cameras in cold climates can help maintain battery efficiency. Select batteries with superior temperature tolerance for optimal performance in varying weather conditions.
Considerations for Specific Trail Camera Models
Different trail camera models may have unique battery requirements and recommendations. Understanding compatibility and manufacturer recommendations is essential for maximizing camera performance and battery life.
- Compatibility with Specific Battery Types and Brands: Some trail camera models may be compatible with specific battery types or brands recommended by the manufacturer. Verify compatibility to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
- Manufacturer Recommendations for Optimal Battery Performance: Manufacturers often provide guidelines and recommendations for battery selection to maximize camera performance. Adhering to these recommendations helps ensure compatibility and longevity.
- User Experiences and Recommendations for Battery Selection Based on Trail Camera Models: User experiences and recommendations offer valuable insights into battery selection for specific trail camera models. Consulting user forums and communities can provide practical advice and recommendations based on real-world usage.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Balancing upfront costs with long-term value is crucial when selecting trail camera batteries. This section evaluates the cost-effectiveness and value proposition of different battery options to help users make informed decisions.
- Comparison of Upfront Costs and Long-Term Expenses for Different Battery Options: Comparing upfront costs and long-term expenses, including replacement frequency, helps assess the overall cost-effectiveness of battery options. While rechargeable batteries may have higher initial costs, their long-term value and savings justify the investment for frequent users.
- Evaluation of Cost-Effectiveness and Value Proposition for Various Battery Brands and Models: Assessing the cost-effectiveness and value proposition of different battery brands and models involves considering factors such as performance, longevity, and reliability. Opting for reputable brands known for quality and durability ensures long-term value and reliability.
- Considerations for Budget-Conscious Consumers and Recommendations for Balancing Cost and Performance: Budget-conscious consumers may prioritize upfront costs but should also consider long-term expenses and reliability when selecting batteries. Choosing mid-range options that strike a balance between cost and performance offers the best value for money over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Considering the environmental impact of trail camera batteries is essential for minimizing ecological footprint and promoting sustainability. This section assesses the environmental implications of different battery types and offers recommendations for eco-friendly practices.
- Assessment of the Environmental Footprint of Different Battery Types: Different battery types have varying environmental footprints, with disposable batteries contributing to waste and pollution. Assessing the ecological impact of batteries helps users make environmentally conscious choices.
- Considerations for Eco-Friendly Battery Options and Sustainability Practices: Opting for eco-friendly battery options, such as rechargeable batteries, reduces waste and promotes sustainability. Implementing practices such as proper disposal and recycling further minimizes environmental impact.
- Recommendations for Minimizing Environmental Impact While Using Trail Camera Batteries: Adopting sustainable practices, such as using rechargeable batteries and recycling old batteries, helps minimize environmental impact while enjoying the benefits of trail camera technology. Educating users on responsible battery usage and disposal promotes environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
In selecting the best batteries for trail cameras requires careful consideration of performance, compatibility, cost, and environmental impact. By evaluating battery options based on independent tests, user reviews, and real-world comparisons, users can make informed decisions that optimize camera performance and longevity.
Maximizing battery life through proper installation, maintenance, and conservation strategies ensures uninterrupted operation and reduced maintenance. Considering specific trail camera models, cost analysis, and environmental sustainability further enhances the selection process. Ultimately, selecting the right batteries is crucial for maximizing trail camera performance while minimizing environmental impact.